Wat is de laagste gemeenschappelijke voorouder in de binaire boom?
De laagste gemeenschappelijke voorouder is het laagste knooppunt in de boom dat zowel n1 als n2 heeft nakomelingen, waarbij n1 en n2 de knooppunten zijn waarvoor we de LCA willen vinden. Daarom is de LCA van een binaire boom met knooppunten n1 en n2 de gedeelde voorouder van n1 en n2 die zich het verst van de wortel bevindt.
Toepassing van de laagste gemeenschappelijke voorouder (LCA):
Om de afstand tussen paren knooppunten in een boom te bepalen: de afstand van n1 tot n2 kan worden berekend als de afstand van de wortel tot n1, plus de afstand van de wortel tot n2, minus tweemaal de afstand van de wortel tot hun laagste gemeenschappelijke Voorouder.
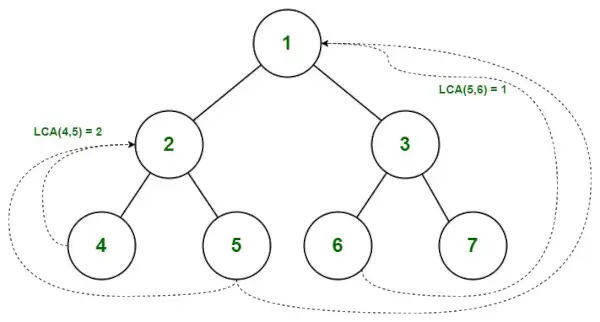
Laagste gemeenschappelijke voorouder in binaire boom
Aanbevolen praktijk Laagste gemeenschappelijke voorouder in een binaire boom Probeer het!
Laagste gemeenschappelijke voorouder in een binaire boom door paden op te slaan van wortel tot n1 en wortel tot n2:
Het idee van deze aanpak is om het pad van de wortel naar n1 en de wortel naar n2 op te slaan in twee afzonderlijke datastructuren. Kijk vervolgens tegelijkertijd naar de waarden die zijn opgeslagen in de datastructuur en zoek naar de eerste mismatch.
Illustratie:
Zoek de LCA van 5 en 6
Pad van wortel naar 5 = { 1, 2, 5 }
Pad van wortel naar 6 = { 1, 3, 6 }
- We beginnen te controleren vanaf index 0. Omdat beide waarden overeenkomen ( pathA[0] = pathB[0] ), gaan we naar de volgende index.
- pathA[1] is niet gelijk aan pathB[1], er is een mismatch, dus we houden rekening met de vorige waarde.
- Daarom is de LCA van (5,6) = 1
Volg de onderstaande stappen om het probleem op te lossen:
- Zoek een pad van de wortel naar n1 en sla dit op in een vector of array.
- Zoek een pad van de wortel naar n2 en sla dit op in een andere vector of array.
- Doorloop beide paden totdat de waarden in arrays hetzelfde zijn. Retourneer het gemeenschappelijke element net vóór de mismatch.
Hieronder volgt de implementatie van het bovenstaande algoritme:
C++
// C++ Program for Lowest Common Ancestor> // in a Binary Tree> // A O(n) solution to find LCA> // of two given values n1 and n2> #include> using> namespace> std;> // A Binary Tree node> struct> Node {> >int> key;> >struct> Node *left, *right;> };> // Utility function creates a new binary tree node with> // given key> Node* newNode(>int> k)> {> >Node* temp =>new> Node;> >temp->sleutel = k;> >temp->links = temp->rechts = NULL;> >return> temp;> }> // Finds the path from root node to given root of the tree,> // Stores the path in a vector path[], returns true if path> // exists otherwise false> bool> findPath(Node* root, vector<>int>>& pad,>int> k)> (root->rechts && findPath(root->right, path, k)))> >return> true>;> >// If not present in subtree rooted with root, remove> >// root from path[] and return false> >path.pop_back();> >return> false>;> > // Returns LCA if node n1, n2 are present in the given> // binary tree, otherwise return -1> int> findLCA(Node* root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> > // Driver program to test above functions> int> main()> {> >// Let us create the Binary Tree shown in above diagram.> >Node* root = newNode(1);> >root->left = newNode(2);> >root->rechts = newNode(3);> >root->links->links = newNode(4);> >root->links->rechts = newNode(5);> >root->rechts->links = newNode(6);> >root->rechts->rechts = newNode(7);> >cout <<>'LCA(4, 5) = '> << findLCA(root, 4, 5);> >cout <<>'
LCA(4, 6) = '> << findLCA(root, 4, 6);> >cout <<>'
LCA(3, 4) = '> << findLCA(root, 3, 4);> >cout <<>'
LCA(2, 4) = '> << findLCA(root, 2, 4);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Java
// Java Program for Lowest Common Ancestor> // in a Binary Tree> // A O(n) solution to find LCA of> // two given values n1 and n2> import> java.util.ArrayList;> import> java.util.List;> // A Binary Tree node> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node left, right;> >Node(>int> value)> >{> >data = value;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> public> class> BT_NoParentPtr_Solution1 {> >Node root;> >private> List path1 =>new> ArrayList();> >private> List path2 =>new> ArrayList();> >// Finds the path from root node to given root of the> >// tree.> >int> findLCA(>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >path1.clear();> >path2.clear();> >return> findLCAInternal(root, n1, n2);> >}> >private> int> findLCAInternal(Node root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >if> (!findPath(root, n1, path1)> >|| !findPath(root, n2, path2)) {> >System.out.println((path1.size()>>0>)> >?>'n1 is present'> >:>'n1 is missing'>);> >System.out.println((path2.size()>>0>)> >?>'n2 is present'> >:>'n2 is missing'>);> >return> ->1>;> >}> >int> i;> >for> (i =>0>; i i++) { // System.out.println(path1.get(i) + ' ' + // path2.get(i)); if (!path1.get(i).equals(path2.get(i))) break; } return path1.get(i - 1); } // Finds the path from root node to given root of the // tree, Stores the path in a vector path[], returns // true if path exists otherwise false private boolean findPath(Node root, int n, List path) { // base case if (root == null) { return false; } // Store this node . The node will be removed if // not in path from root to n. path.add(root.data); if (root.data == n || findPath(root.left, n, path) || findPath(root.right, n, path)) { return true; } // If not present in subtree rooted with root, // remove root from path[] and return false path.remove(path.size() - 1); return false; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { BT_NoParentPtr_Solution1 tree = new BT_NoParentPtr_Solution1(); tree.root = new Node(1); tree.root.left = new Node(2); tree.root.right = new Node(3); tree.root.left.left = new Node(4); tree.root.left.right = new Node(5); tree.root.right.left = new Node(6); tree.root.right.right = new Node(7); System.out.println('LCA(4, 5) = ' + tree.findLCA(4, 5)); System.out.println('LCA(4, 6) = ' + tree.findLCA(4, 6)); System.out.println('LCA(3, 4) = ' + tree.findLCA(3, 4)); System.out.println('LCA(2, 4) = ' + tree.findLCA(2, 4)); } } // This code is contributed by Sreenivasulu Rayanki.> |
>
>
Python3
# Python Program for Lowest Common Ancestor in a Binary Tree> # O(n) solution to find LCS of two given values n1 and n2> # A binary tree node> class> Node:> ># Constructor to create a new binary node> >def> __init__(>self>, key):> >self>.key>=> key> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> # Finds the path from root node to given root of the tree.> # Stores the path in a list path[], returns true if path> # exists otherwise false> def> findPath(root, path, k):> ># Baes Case> >if> root>is> None>:> >return> False> ># Store this node is path vector. The node will be> ># removed if not in path from root to k> >path.append(root.key)> ># See if the k is same as root's key> >if> root.key>=>=> k:> >return> True> ># Check if k is found in left or right sub-tree> >if> ((root.left !>=> None> and> findPath(root.left, path, k))>or> >(root.right !>=> None> and> findPath(root.right, path, k))):> >return> True> ># If not present in subtree rooted with root, remove> ># root from path and return False> >path.pop()> >return> False> # Returns LCA if node n1 , n2 are present in the given> # binary tree otherwise return -1> def> findLCA(root, n1, n2):> ># To store paths to n1 and n2 fromthe root> >path1>=> []> >path2>=> []> ># Find paths from root to n1 and root to n2.> ># If either n1 or n2 is not present , return -1> >if> (>not> findPath(root, path1, n1)>or> not> findPath(root, path2, n2)):> >return> ->1> ># Compare the paths to get the first different value> >i>=> 0> >while>(i <>len>(path1)>and> i <>len>(path2)):> >if> path1[i] !>=> path2[i]:> >break> >i>+>=> 1> >return> path1[i>->1>]> # Driver program to test above function> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> > ># Let's create the Binary Tree shown in above diagram> >root>=> Node(>1>)> >root.left>=> Node(>2>)> >root.right>=> Node(>3>)> >root.left.left>=> Node(>4>)> >root.left.right>=> Node(>5>)> >root.right.left>=> Node(>6>)> >root.right.right>=> Node(>7>)> > >print>(>'LCA(4, 5) = %d'> %> (findLCA(root,>4>,>5>,)))> >print>(>'LCA(4, 6) = %d'> %> (findLCA(root,>4>,>6>)))> >print>(>'LCA(3, 4) = %d'> %> (findLCA(root,>3>,>4>)))> >print>(>'LCA(2, 4) = %d'> %> (findLCA(root,>2>,>4>)))> # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> |
>
>
C#
// C# Program for Lowest Common> // Ancestor in a Binary Tree> // A O(n) solution to find LCA> // of two given values n1 and n2> using> System.Collections;> using> System;> // A Binary Tree node> class> Node {> >public> int> data;> >public> Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> value)> >{> >data = value;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> public> class> BT_NoParentPtr_Solution1 {> >Node root;> >private> ArrayList path1 =>new> ArrayList();> >private> ArrayList path2 =>new> ArrayList();> >// Finds the path from root> >// node to given root of the> >// tree.> >int> findLCA(>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >path1.Clear();> >path2.Clear();> >return> findLCAInternal(root, n1, n2);> >}> >private> int> findLCAInternal(Node root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >if> (!findPath(root, n1, path1)> >|| !findPath(root, n2, path2)) {> >Console.Write((path1.Count>0)> >?>'n1 is present'> >:>'n1 is missing'>);> >Console.Write((path2.Count>0)> >?>'n2 is present'> >:>'n2 is missing'>);> >return> -1;> >}> >int> i;> >for> (i = 0; i i++) { // System.out.println(path1.get(i) // + ' ' + path2.get(i)); if ((int)path1[i] != (int)path2[i]) break; } return (int)path1[i - 1]; } // Finds the path from root node // to given root of the tree, // Stores the path in a vector // path[], returns true if path // exists otherwise false private bool findPath(Node root, int n, ArrayList path) { // base case if (root == null) { return false; } // Store this node . The node // will be removed if not in // path from root to n. path.Add(root.data); if (root.data == n) { return true; } if (root.left != null && findPath(root.left, n, path)) { return true; } if (root.right != null && findPath(root.right, n, path)) { return true; } // If not present in subtree // rooted with root, remove root // from path[] and return false path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1); return false; } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { BT_NoParentPtr_Solution1 tree = new BT_NoParentPtr_Solution1(); tree.root = new Node(1); tree.root.left = new Node(2); tree.root.right = new Node(3); tree.root.left.left = new Node(4); tree.root.left.right = new Node(5); tree.root.right.left = new Node(6); tree.root.right.right = new Node(7); Console.Write('LCA(4, 5) = ' + tree.findLCA(4, 5)); Console.Write('
LCA(4, 6) = ' + tree.findLCA(4, 6)); Console.Write('
LCA(3, 4) = ' + tree.findLCA(3, 4)); Console.Write('
LCA(2, 4) = ' + tree.findLCA(2, 4)); } } // This code is contributed by Rutvik_56> |
>
>
Javascript
> >// JavaScript Program for Lowest Common> >// Ancestor in a Binary Tree> >// A O(n) solution to find LCA of> >// two given values n1 and n2> > >class Node> >{> >constructor(value) {> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >this>.data = value;> >}> >}> > >let root;> >let path1 = [];> >let path2 = [];> > >// Finds the path from root node to given root of the tree.> >function> findLCA(n1, n2) {> >path1 = [];> >path2 = [];> >return> findLCAInternal(root, n1, n2);> >}> > >function> findLCAInternal(root, n1, n2) {> > >if> (!findPath(root, n1, path1) || !findPath(root, n2, path2))> >{> >document.write((path1.length>0) ?> >'n1 is present'> :>'n1 is missing'>);> >document.write((path2.length>0) ?> >'n2 is present'> :>'n2 is missing'>);> >return> -1;> >}> > >let i;> >for> (i = 0; i // System.out.println(path1.get(i) + ' ' + path2.get(i)); if (path1[i] != path2[i]) break; } return path1[i-1]; } // Finds the path from root node to // given root of the tree, Stores the // path in a vector path[], returns true // if path exists otherwise false function findPath(root, n, path) { // base case if (root == null) { return false; } // Store this node . The node will be removed if // not in path from root to n. path.push(root.data); if (root.data == n) { return true; } if (root.left != null && findPath(root.left, n, path)) { return true; } if (root.right != null && findPath(root.right, n, path)) { return true; } // If not present in subtree rooted with root, // remove root from // path[] and return false path.pop(); return false; } root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.left = new Node(6); root.right.right = new Node(7); document.write('LCA(4, 5) = ' + findLCA(4,5) + ''); document.write('LCA(4, 6) = ' + findLCA(4,6) + ''); document.write('LCA(3, 4) = ' + findLCA(3,4) + ''); document.write('LCA(2, 4) = ' + findLCA(2,4));> |
>
>Uitvoer
LCA(4, 5) = 2 LCA(4, 6) = 1 LCA(3, 4) = 1 LCA(2, 4) = 2>
Tijdcomplexiteit: OP). De boom wordt tweemaal doorlopen en vervolgens worden padarrays vergeleken.
Hulpruimte: OP). Extra ruimte voor pad1 en pad2.
Laagste gemeenschappelijke voorouder in een binaire boom door enkele verplaatsing:
Het idee is om de boom te doorkruisen, beginnend bij de wortel. Als een van de gegeven sleutels (n1 en n2) overeenkomt met de root, dan is de root LCA (ervan uitgaande dat beide sleutels aanwezig zijn). Als de wortel niet overeenkomt met een van de sleutels, herhalen we dit voor de linker en rechter subboom.
- Het knooppunt waarvan één sleutel aanwezig is in de linker subboom en de andere sleutel aanwezig is in de rechter subboom, is de LCA.
- Als beide sleutels in de linker subboom liggen, heeft de linker subboom ook LCA,
- Anders ligt de LCA in de juiste subboom.
Illustratie:
Zoek de LCA van 5 en 6
Wortel verwijst naar het knooppunt met waarde 1, omdat de waarde ervan niet overeenkomt met { 5, 6 }. We zoeken de sleutel in de linker subboom en de rechter subboom.
- Linker subboom:
- Nieuwe wortel = { 2 } ≠ 5 of 6, daarom zullen we onze recursie voortzetten
- New Root = { 4 }, de linker en rechter subboom zijn nul, we zullen NULL retourneren voor deze aanroep
- Nieuwe wortel = { 5 }, waarde komt overeen met 5, dus retourneert het knooppunt met waarde 5
- De functieaanroep voor root met waarde 2 retourneert een waarde van 5
- Rechter subboom:
- Wortel = { 3 } ≠ 5 of 6 vandaar dat we onze recursie voortzetten
- Root = { 6 } = 5 of 6 , we zullen dit knooppunt retourneren met waarde 6
- Root = { 7 } ≠ 5 of 6, we retourneren NULL
- Dus de functieaanroep voor root met waarde 3 retourneert een knooppunt met waarde 6
- Omdat zowel de linker subboom als de rechter subboom van het knooppunt met waarde 1 niet NULL is, is 1 de LCA
Volg de onderstaande stappen om het probleem op te lossen:
- We geven de wortel door aan een helperfunctie en controleren of de waarde van de wortel overeenkomt met n1 en n2.
- Indien JA, retourneer de root
- anders recursieve aanroep in de linker en rechter subboom
- In principe doen we pre-order traversal, eerst controleren we of de root->waarde overeenkomt met n1 of n2. Ga vervolgens door de linker en rechter deelboom.
- Als er een root is die één NULL- en een andere NON-NULL-waarde retourneert, zullen we de overeenkomstige NON-NULL-waarde voor dat knooppunt retourneren.
- Het knooppunt dat beide NON-NULL-waarden retourneert voor zowel de linker als de rechter subboom, is onze Lowest Common Ancestor.
Hieronder vindt u de implementatie van bovenstaande aanpak.
C++
/* C++ Program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one traversal> >* of Binary Tree */> #include> using> namespace> std;> // A Binary Tree Node> struct> Node {> >struct> Node *left, *right;> >int> key;> };> // Utility function to create a new tree Node> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >Node* temp =>new> Node;> >temp->sleutel = sleutel;> >temp->links = temp->rechts = NULL;> >return> temp;> }> // This function returns pointer to LCA of two given values> // n1 and n2. This function assumes that n1 and n2 are> // present in Binary Tree> struct> Node* findLCA(>struct> Node* root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> > >// Base case> >if> (root == NULL)> >return> NULL;> >// If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key, report> >// the presence by returning root (Note that if a key is> >// ancestor of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA> >if> (root->toets == n1> // Driver program to test above functions> int> main()> {> >// Let us create binary tree given in the above example> >Node* root = newNode(1);> >root->left = newNode(2);> >root->rechts = newNode(3);> >root->links->links = newNode(4);> >root->links->rechts = newNode(5);> >root->rechts->links = newNode(6);> >root->rechts->rechts = newNode(7);> >cout <<>'LCA(4, 5) = '> cout << '
LCA(4, 6) = ' cout << '
LCA(3, 4) = ' cout << '
LCA(2, 4) = ' return 0; } // This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)> |
>
>
C
// C Program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one traversalof> // Binary Tree> #include> #include> // A Binary Tree Node> typedef> struct> Node {> >struct> Node *left, *right;> >int> key;> } Node;> // Utility function to create a new tree Node> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >Node* temp = (Node*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(Node));> >temp->sleutel = sleutel;> >temp->links = temp->rechts = NULL;> >return> temp;> }> // This function returns pointer to LCA of two given values> // n1 and n2. This function assumes that n1 and n2 are> // present in Binary Tree> Node* findLCA(Node* root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> > >// Base case> >if> (root == NULL)> >return> NULL;> >// If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key, report> >// the presence by returning root (Note that if a key is> >// ancestor of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA> >if> (root->toets == n1> // Driver program to test above functions> int> main()> {> >// Let us create binary tree given in the above example> >Node* root = newNode(1);> >root->left = newNode(2);> >root->rechts = newNode(3);> >root->links->links = newNode(4);> >root->links->rechts = newNode(5);> >root->rechts->links = newNode(6);> >root->rechts->rechts = newNode(7);> >printf>(>'LCA(4, 5) = %d'>, findLCA(root, 4, 5)->toets);> >printf>(>'
LCA(4, 6) = %d'>, findLCA(root, 4, 6)->toets);> >printf>(>'
LCA(3, 4) = %d'>, findLCA(root, 3, 4)->toets);> >printf>(>'
LCA(2, 4) = %d'>, findLCA(root, 2, 4)->toets);> >return> 0;> }> // This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)> |
>
>
Java
// Java implementation to find lowest common ancestor of> // n1 and n2 using one traversal of binary tree> /* Class containing left and right child of current> >node and key value*/> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> item)> >{> >data = item;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> public> class> BinaryTree {> >// Root of the Binary Tree> >Node root;> >Node findLCA(>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >return> findLCA(root, n1, n2);> >}> >// This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> >// values n1 and n2. This function assumes that n1 and> >// n2 are present in Binary Tree> >Node findLCA(Node node,>int> n1,>int> n2)> >> >// Base case> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> null>;> >// If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key,> >// report the presence by returning root (Note that> >// if a key is ancestor of other, then the ancestor> >// key becomes LCA> >if> (node.data == n1> >/* Driver program to test above functions */> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >BinaryTree tree =>new> BinaryTree();> >tree.root =>new> Node(>1>);> >tree.root.left =>new> Node(>2>);> >tree.root.right =>new> Node(>3>);> >tree.root.left.left =>new> Node(>4>);> >tree.root.left.right =>new> Node(>5>);> >tree.root.right.left =>new> Node(>6>);> >tree.root.right.right =>new> Node(>7>);> >System.out.println(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(>4>,>5>).data);> >System.out.println(>'LCA(4, 6) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(>4>,>6>).data);> >System.out.println(>'LCA(3, 4) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(>3>,>4>).data);> >System.out.println(>'LCA(2, 4) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(>2>,>4>).data);> >}> }> |
>
>
Python3
# Python program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one> # traversal of Binary tree> # A binary tree node> class> Node:> ># Constructor to create a new tree node> >def> __init__(>self>, key):> >self>.key>=> key> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> # This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> # values n1 and n2> # This function assumes that n1 and n2 are present in> # Binary Tree> def> findLCA(root, n1, n2):> ># Base Case> >if> root>is> None>:> >return> None> ># If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key, report> ># the presence by returning root (Note that if a key is> ># ancestor of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA> >if> root.key>=>=> n1>or> root.key>=>=> n2:> >return> root> ># Look for keys in left and right subtrees> >left_lca>=> findLCA(root.left, n1, n2)> >right_lca>=> findLCA(root.right, n1, n2)> ># If both of the above calls return Non-NULL, then one key> ># is present in once subtree and other is present in other,> ># So this node is the LCA> >if> left_lca>and> right_lca:> >return> root> ># Otherwise check if left subtree or right subtree is LCA> >return> left_lca>if> left_lca>is> not> None> else> right_lca> # Driver code> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> > ># Let us create a binary tree given in the above example> >root>=> Node(>1>)> >root.left>=> Node(>2>)> >root.right>=> Node(>3>)> >root.left.left>=> Node(>4>)> >root.left.right>=> Node(>5>)> >root.right.left>=> Node(>6>)> >root.right.right>=> Node(>7>)> >print>(>'LCA(4, 5) = '>, findLCA(root,>4>,>5>).key)> >print>(>'LCA(4, 6) = '>, findLCA(root,>4>,>6>).key)> >print>(>'LCA(3, 4) = '>, findLCA(root,>3>,>4>).key)> >print>(>'LCA(2, 4) = '>, findLCA(root,>2>,>4>).key)> # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> |
>
>
C#
// C# implementation to find lowest common> // ancestor of n1 and n2 using one traversal> // of binary tree> using> System;> // Class containing left and right> // child of current node and key value> public> class> Node {> >public> int> data;> >public> Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> item)> >{> >data = item;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> class> BinaryTree {> >// Root of the Binary Tree> >Node root;> >Node findLCA(>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >return> findLCA(root, n1, n2);> >}> >// This function returns pointer to LCA> >// of two given values n1 and n2. This> >// function assumes that n1 and n2 are> >// present in Binary Tree> >Node findLCA(Node node,>int> n1,>int> n2)> > node.data == n2)> >return> node;> >// Look for keys in left and right subtrees> >Node left_lca = findLCA(node.left, n1, n2);> >Node right_lca = findLCA(node.right, n1, n2);> >// If both of the above calls return Non-NULL,> >// then one key is present in once subtree> >// and other is present in other, So this> >// node is the LCA> >if> (left_lca !=>null> && right_lca !=>null>)> >return> node;> >// Otherwise check if left subtree or> >// right subtree is LCA> >return> (left_lca !=>null>) ? left_lca : right_lca;> >> >// Driver code> >public> static> void> Main(>string>[] args)> >{> >BinaryTree tree =>new> BinaryTree();> >tree.root =>new> Node(1);> >tree.root.left =>new> Node(2);> >tree.root.right =>new> Node(3);> >tree.root.left.left =>new> Node(4);> >tree.root.left.right =>new> Node(5);> >tree.root.right.left =>new> Node(6);> >tree.root.right.right =>new> Node(7);> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(4, 5).data);> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(4, 6) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(4, 6).data);> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(3, 4) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(3, 4).data);> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(2, 4) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(2, 4).data);> >}> }> // This code is contributed by pratham76> |
>
>
Javascript
> >// JavaScript implementation to find> >// lowest common ancestor of> >// n1 and n2 using one traversal of binary tree> > >class Node> >{> >constructor(item) {> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >this>.data = item;> >}> >}> > >//Root of the Binary Tree> >let root;> > >function> findlCA(n1, n2)> >{> >return> findLCA(root, n1, n2);> >}> > >// This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> >// values n1 and n2. This function assumes that n1 and> >// n2 are present in Binary Tree> >function> findLCA(node, n1, n2)> >> > >root =>new> Node(1);> >root.left =>new> Node(2);> >root.right =>new> Node(3);> >root.left.left =>new> Node(4);> >root.left.right =>new> Node(5);> >root.right.left =>new> Node(6);> >root.right.right =>new> Node(7);> >document.write(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> +> >findlCA(4, 5).data +>''>);> >document.write(>'LCA(4, 6) = '> +> >findlCA(4, 6).data +>''>);> >document.write(>'LCA(3, 4) = '> +> >findlCA(3, 4).data +>''>);> >document.write(>'LCA(2, 4) = '> +> >findlCA(2, 4).data +>''>);> > > |
>
>Uitvoer
LCA(4, 5) = 2 LCA(4, 6) = 1 LCA(3, 4) = 1 LCA(2, 4) = 2>
Tijdcomplexiteit : O(N), aangezien de methode een eenvoudige boomdoorloop op een bottom-up manier uitvoert.
Hulpruimte: O(H), waarbij H de hoogte van de boom is.
Opmerking: De bovenstaande methode gaat ervan uit dat sleutels zijn aanwezig in de binaire boom . Als de ene sleutel aanwezig is en de andere afwezig, retourneert het de huidige sleutel als LCA (idealiter zou dit NULL moeten zijn). We kunnen deze methode uitbreiden om alle gevallen af te handelen door eerst te controleren of n1 en n2 in de boom aanwezig zijn en vervolgens de LCA van n1 en n2 te vinden. Om te controleren of het knooppunt aanwezig is in de binaire boom of niet, doorloopt u de boom afzonderlijk voor zowel n1- als n2-knooppunten.
C++
/* C++ program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one traversal> >of Binary Tree. It handles all cases even when n1 or n2> >is not there in Binary Tree */> #include> using> namespace> std;> // A Binary Tree Node> struct> Node {> >struct> Node *left, *right;> >int> key;> };> // Utility function to create a new tree Node> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >Node* temp =>new> Node;> >temp->sleutel = sleutel;> >temp->links = temp->rechts = NULL;> >return> temp;> }> // This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> // valuesn1 and n2.> struct> Node* findLCAUtil(>struct> Node* root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> > // Returns true if key k is present in tree rooted with root> bool> find(Node* root,>int> k)> find(root->rechts, k))> >return> true>;> >// Else return false> >return> false>;> > // This function returns LCA of n1 and n2 only if both n1> // and n2 are present in tree, otherwise returns NULL;> Node* findLCA(Node* root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> {> >// Return LCA only if both n1 and n2 are present in tree> >if> (find(root, n1) and find(root, n2))> >return> findLCAUtil(root, n1, n2);> >// Else return NULL> >return> NULL;> }> // Driver program to test above functions> int> main()> {> >// Let us create a binary tree given in the above> >// example> >Node* root = newNode(1);> >root->left = newNode(2);> >root->rechts = newNode(3);> >root->links->links = newNode(4);> >root->links->rechts = newNode(5);> >root->rechts->links = newNode(6);> >root->rechts->rechts = newNode(7);> >Node* lca = findLCA(root, 4, 5);> >if> (lca != NULL)> >cout <<>'LCA(4, 5) = '> else cout << 'Keys are not present '; lca = findLCA(root, 4, 10); if (lca != NULL) cout << '
LCA(4, 10) = ' else cout << '
Keys are not present '; return 0; } // This code is contributed by Kshitij Dwivedi // (kshitijdwivedi28)> |
>
>
Java
// Java implementation to find lowest common ancestor of> // n1 and n2 using one traversal of binary tree> // It also handles cases even when n1 and n2 are not there> // in Tree> /* Class containing left and right child of current node and> >* key */> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> item)> >{> >data = item;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> public> class> BinaryTree {> >// Root of the Binary Tree> >Node root;> >static> boolean> v1 =>false>, v2 =>false>;> >// This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> >// values n1 and n2.> >// v1 is set as true by this function if n1 is found> >// v2 is set as true by this function if n2 is found> >Node findLCAUtil(Node node,>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >// Base case> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> null>;> >// Store result in temp, in case of key match so> >// that we can search for other key also.> >Node temp =>null>;> >// If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key,> >// report the presence by setting v1 or v2 as true> >// and return root (Note that if a key is ancestor> >// of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA)> >if> (node.data == n1) {> >v1 =>true>;> >temp = node;> >}> >if> (node.data == n2) {> >v2 =>true>;> >temp = node;> >}> >// Look for keys in left and right subtrees> >Node left_lca = findLCAUtil(node.left, n1, n2);> >Node right_lca = findLCAUtil(node.right, n1, n2);> >if> (temp !=>null>)> >return> temp;> >// If both of the above calls return Non-NULL, then> >// one key is present in once subtree and other is> >// present in other, So this node is the LCA> >if> (left_lca !=>null> && right_lca !=>null>)> >return> node;> >// Otherwise check if left subtree or right subtree> >// is LCA> >return> (left_lca !=>null>) ? left_lca : right_lca;> >}> >// Finds lca of n1 and n2 under the subtree rooted with> >// 'node'> >Node findLCA(>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >// Initialize n1 and n2 as not visited> >v1 =>false>;> >v2 =>false>;> >// Find lca of n1 and n2 using the technique> >// discussed above> >Node lca = findLCAUtil(root, n1, n2);> >// Return LCA only if both n1 and n2 are present in> >// tree> >if> (v1 && v2)> >return> lca;> >// Else return NULL> >return> null>;> >}> >/* Driver program to test above functions */> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >BinaryTree tree =>new> BinaryTree();> >tree.root =>new> Node(>1>);> >tree.root.left =>new> Node(>2>);> >tree.root.right =>new> Node(>3>);> >tree.root.left.left =>new> Node(>4>);> >tree.root.left.right =>new> Node(>5>);> >tree.root.right.left =>new> Node(>6>);> >tree.root.right.right =>new> Node(>7>);> >Node lca = tree.findLCA(>4>,>5>);> >if> (lca !=>null>)> >System.out.println(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> + lca.data);> >else> >System.out.println(>'Keys are not present'>);> >lca = tree.findLCA(>4>,>10>);> >if> (lca !=>null>)> >System.out.println(>'LCA(4, 10) = '> + lca.data);> >else> >System.out.println(>'Keys are not present'>);> >}> }> |
>
>
Python3
''' Program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one traversal of> >Binary tree> It handles all cases even when n1 or n2 is not there in tree> '''> # A binary tree node> class> Node:> ># Constructor to create a new node> >def> __init__(>self>, key):> >self>.key>=> key> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> # This function return pointer to LCA of two given values> # n1 and n2> # v1 is set as true by this function if n1 is found> # v2 is set as true by this function if n2 is found> def> findLCAUtil(root, n1, n2, v):> ># Base Case> >if> root>is> None>:> >return> None> ># IF either n1 or n2 matches ith root's key, report> ># the presence by setting v1 or v2 as true and return> ># root (Note that if a key is ancestor of other, then> ># the ancestor key becomes LCA)> >if> root.key>=>=> n1:> >v[>0>]>=> True> >return> root> >if> root.key>=>=> n2:> >v[>1>]>=> True> >return> root> ># Look for keys in left and right subtree> >left_lca>=> findLCAUtil(root.left, n1, n2, v)> >right_lca>=> findLCAUtil(root.right, n1, n2, v)> ># If both of the above calls return Non-NULL, then one key> ># is present in once subtree and other is present in other,> ># So this node is the LCA> >if> left_lca>and> right_lca:> >return> root> ># Otherwise check if left subtree or right subtree is LCA> >return> left_lca>if> left_lca>is> not> None> else> right_lca> def> find(root, k):> ># Base Case> >if> root>is> None>:> >return> False> ># If key is present at root, or if left subtree or right> ># subtree , return true> >if> (root.key>=>=> k>or> find(root.left, k)>or> >find(root.right, k)):> >return> True> ># Else return false> >return> False> # This function returns LCA of n1 and n2 on value if both> # n1 and n2 are present in tree, otherwise returns None> def> findLCA(root, n1, n2):> ># Initialize n1 and n2 as not visited> >v>=> [>False>,>False>]> ># Find lca of n1 and n2 using the technique discussed above> >lca>=> findLCAUtil(root, n1, n2, v)> ># Returns LCA only if both n1 and n2 are present in tree> >if> (v[>0>]>and> v[>1>]>or> v[>0>]>and> find(lca, n2)>or> v[>1>]>and> >find(lca, n1)):> >return> lca> ># Else return None> >return> None> # Driver program to test above function> root>=> Node(>1>)> root.left>=> Node(>2>)> root.right>=> Node(>3>)> root.left.left>=> Node(>4>)> root.left.right>=> Node(>5>)> root.right.left>=> Node(>6>)> root.right.right>=> Node(>7>)> lca>=> findLCA(root,>4>,>5>)> if> lca>is> not> None>:> >print>(>'LCA(4, 5) = '>, lca.key)> else>:> >print>(>'Keys are not present'>)> lca>=> findLCA(root,>4>,>10>)> if> lca>is> not> None>:> >print>(>'LCA(4,10) = '>, lca.key)> else>:> >print>(>'Keys are not present'>)> # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> |
>
>
C#
using> System;> // c# implementation to find lowest common ancestor of> // n1 and n2 using one traversal of binary tree> // It also handles cases even when n1 and n2 are not there> // in Tree> /* Class containing left and right child of current node and> >* key */> public> class> Node {> >public> int> data;> >public> Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> item)> >{> >data = item;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> public> class> BinaryTree {> >// Root of the Binary Tree> >public> Node root;> >public> static> bool> v1 =>false>, v2 =>false>;> >// This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> >// values n1 and n2.> >// v1 is set as true by this function if n1 is found> >// v2 is set as true by this function if n2 is found> >public> virtual> Node findLCAUtil(Node node,>int> n1,> >int> n2)> >{> >// Base case> >if> (node ==>null>) {> >return> null>;> >}> >// Store result in temp, in case of key match so> >// that we can search for other key also.> >Node temp =>null>;> >// If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key,> >// report the presence by setting v1 or v2 as true> >// and return root (Note that if a key is ancestor> >// of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA)> >if> (node.data == n1) {> >v1 =>true>;> >temp = node;> >}> >if> (node.data == n2) {> >v2 =>true>;> >temp = node;> >}> >// Look for keys in left and right subtrees> >Node left_lca = findLCAUtil(node.left, n1, n2);> >Node right_lca = findLCAUtil(node.right, n1, n2);> >if> (temp !=>null>) {> >return> temp;> >}> >// If both of the above calls return Non-NULL, then> >// one key is present in once subtree and other is> >// present in other, So this node is the LCA> >if> (left_lca !=>null> && right_lca !=>null>) {> >return> node;> >}> >// Otherwise check if left subtree or right subtree> >// is LCA> >return> (left_lca !=>null>) ? left_lca : right_lca;> >}> >// Finds lca of n1 and n2 under the subtree rooted with> >// 'node'> >public> virtual> Node findLCA(>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >// Initialize n1 and n2 as not visited> >v1 =>false>;> >v2 =>false>;> >// Find lca of n1 and n2 using the technique> >// discussed above> >Node lca = findLCAUtil(root, n1, n2);> >// Return LCA only if both n1 and n2 are present in> >// tree> >if> (v1 && v2) {> >return> lca;> >}> >// Else return NULL> >return> null>;> >}> >/* Driver program to test above functions */> >public> static> void> Main(>string>[] args)> >{> >BinaryTree tree =>new> BinaryTree();> >tree.root =>new> Node(1);> >tree.root.left =>new> Node(2);> >tree.root.right =>new> Node(3);> >tree.root.left.left =>new> Node(4);> >tree.root.left.right =>new> Node(5);> >tree.root.right.left =>new> Node(6);> >tree.root.right.right =>new> Node(7);> >Node lca = tree.findLCA(4, 5);> >if> (lca !=>null>) {> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> + lca.data);> >}> >else> {> >Console.WriteLine(>'Keys are not present'>);> >}> >lca = tree.findLCA(4, 10);> >if> (lca !=>null>) {> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(4, 10) = '> + lca.data);> >}> >else> {> >Console.WriteLine(>'Keys are not present'>);> >}> >}> }> // This code is contributed by Shrikant13> |
>
>
Javascript
> // JavaScript implementation to find lowest> // common ancestor of n1 and n2 using one> // traversal of binary tree. It also handles> // cases even when n1 and n2 are not there in Tree> // Class containing left and right child> // of current node and key> class Node> {> >constructor(item)> >{> >this>.data = item;> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >}> }> class BinaryTree{> > // Root of the Binary Tree> constructor()> {> >this>.root =>null>;> >this>.v1 =>false>;> >this>.v2 =>false>;> }> // This function returns pointer to LCA> // of two given values n1 and n2.> // v1 is set as true by this function> // if n1 is found> // v2 is set as true by this function> // if n2 is found> findLCAUtil(node, n1, n2)> {> > >// Base case> >if> (node ==>null>)> >{> >return> null>;> >}> > >// Store result in temp, in case of> >// key match so that we can search> >// for other key also.> >var> temp =>null>;> > >// If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key,> >// report the presence by setting v1 or v2 as> >// true and return root (Note that if a key> >// is ancestor of other, then the ancestor> >// key becomes LCA)> >if> (node.data == n1)> >{> >this>.v1 =>true>;> >temp = node;> >}> >if> (node.data == n2)> >{> >this>.v2 =>true>;> >temp = node;> >}> > >// Look for keys in left and right subtrees> >var> left_lca =>this>.findLCAUtil(node.left, n1, n2);> >var> right_lca =>this>.findLCAUtil(node.right, n1, n2);> > >if> (temp !=>null>)> >{> >return> temp;> >}> > >// If both of the above calls return Non-NULL,> >// then one key is present in once subtree and> >// other is present in other, So this node is the LCA> >if> (left_lca !=>null> && right_lca !=>null>)> >{> >return> node;> >}> > >// Otherwise check if left subtree or> >// right subtree is LCA> >return> left_lca !=>null> ? left_lca : right_lca;> }> // Finds lca of n1 and n2 under the> // subtree rooted with 'node'> findLCA(n1, n2)> {> > >// Initialize n1 and n2 as not visited> >this>.v1 =>false>;> >this>.v2 =>false>;> > >// Find lca of n1 and n2 using the> >// technique discussed above> >var> lca =>this>.findLCAUtil(>this>.root, n1, n2);> > >// Return LCA only if both n1 and n2> >// are present in tree> >if> (>this>.v1 &&>this>.v2)> >{> >return> lca;> >}> > >// Else return NULL> >return> null>;> }> }> // Driver code> var> tree =>new> BinaryTree();> tree.root =>new> Node(1);> tree.root.left =>new> Node(2);> tree.root.right =>new> Node(3);> tree.root.left.left =>new> Node(4);> tree.root.left.right =>new> Node(5);> tree.root.right.left =>new> Node(6);> tree.root.right.right =>new> Node(7);> var> lca = tree.findLCA(4, 5);> if> (lca !=>null>)> {> >document.write(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> +> >lca.data +>' '>);> }>else> {> >document.write(>'Keys are not present'> +>' '>);> }> lca = tree.findLCA(4, 10);> if> (lca !=>null>)> {> >document.write(>'LCA(4, 10) = '> +> >lca.data +>' '>);> }> else> {> >document.write(>'Keys are not present'> +>' '>);> }> // This code is contributed by rdtank> > |
>
>Uitvoer
LCA(4, 5) = 2 Keys are not present>
Tijdcomplexiteit : O(N), aangezien de methode een eenvoudige boomdoorloop op een bottom-up manier uitvoert.
Hulpruimte: O(H), waarbij h de hoogte van de boom is.
Een hulpgegevensstructuur gebruiken (hashtabel):
The basic idea behind the 'Using an auxiliary data structure' approach for finding the lowest common ancestor of two nodes in a binary tree is to use a hash table or a map to store the parent pointers of each node. Once we have the parent pointers, we can traverse up from the first node and add all its ancestors to a set or a list. Then we can traverse up from the second node and check if each ancestor is already in the set or the list. The first ancestor that is already in the set or the list is the lowest common ancestor.>
Volg de stappen om de bovenstaande aanpak te implementeren:
- Maak een hashtabel of een kaart om de ouderaanwijzers van elk knooppunt in de binaire boom op te slaan.
- Doorkruis de binaire boom en vul de hashtabel of de kaart met de ouderaanwijzers voor elk knooppunt.
- Begin vanaf het eerste knooppunt en doorloop de boom omhoog en voeg elke voorouder toe aan een set of lijst.
- Begin vanaf het tweede knooppunt door de boom heen en controleer of elke voorouder al in de set of de lijst voorkomt. De eerste voorouder die al in de set of de lijst voorkomt, is de laagste gemeenschappelijke voorouder.
- Als er geen gemeenschappelijke voorouder wordt gevonden, retourneer dan null of een andere waarde die de afwezigheid van een gemeenschappelijke voorouder aangeeft.
Hieronder vindt u de implementatie van de bovenstaande aanpak:
C++
// C++ code to implement above approach> #include> #include> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Definition of a binary tree node> struct> Node {> >int> data;> >Node* left;> >Node* right;> };> // Function to create a new binary tree node> Node* newNode(>int> data)> {> >Node* node =>new> Node;> >node->gegevens = gegevens;> >node->links = NULL;> >node->rechts = NULL;> >return> (node);> }> // Function to build a hash table or a map of parent> // pointers for each node in the tree> unordered_map buildParentMap(Node* root)> {> >unordered_map parentMap;> >parentMap[root] = NULL;> >vector queue = { root };> >while> (!queue.empty()) {> >Node* node = queue.front();> >queue.erase(queue.begin());> >if> (node->links) {> >parentMap[node->links] = knooppunt;> >queue.push_back(node->links);> >}> >if> (node->rechts) {> >parentMap[node->rechts] = knooppunt;> >queue.push_back(node->rechts);> >}> >}> >return> parentMap;> }> // Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two nodes> // using an auxiliary data structure> int> findLCA(Node* root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> {> >// Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers for> >// each node in the tree> >unordered_map parentMap> >= buildParentMap(root);> >// Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> >Node* p = NULL;> >Node* q = NULL;> >vector queue = { root };> >while> (!queue.empty()) {> >Node* node = queue.front();> >queue.erase(queue.begin());> >if> (node->gegeven == n1) {> >p = node;> >}> >if> (node->gegevens == n2) {> >q = node;> >}> >if> (node->links) {> >queue.push_back(node->links);> >}> >if> (node->rechts) {> >queue.push_back(node->rechts);> >}> >}> >// Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set or a> >// list> >set ancestors;> >while> (p) {> >ancestors.insert(p);> >p = parentMap[p];> >}> >// Traverse up from the second node and check if each> >// ancestor is already in the set or the list> >while> (q) {> >if> (ancestors.find(q) != ancestors.end()) {> >return> q> >->gegevens;>// The first ancestor that is> >// already in the set or the list is> >// the lowest common ancestor> >}> >q = parentMap[q];> >}> >return> -1;>// No common ancestor found> }> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >Node* root = newNode(1);> >root->left = newNode(2);> >root->rechts = newNode(3);> >root->links->links = newNode(4);> >root->links->rechts = newNode(5);> >root->rechts->links = newNode(6);> >root->rechts->rechts = newNode(7);> >cout <<>'LCA(4, 5) = '> << findLCA(root, 4, 5) << endl;> >cout <<>'LCA(4, 6) = '> << findLCA(root, 4, 6) << endl;> >cout <<>'LCA(3,4) = '> << findLCA(root, 3, 4) << endl;> >cout <<>'LCA(2, 4) = '> << findLCA(root, 2, 4) << endl;> >return> 0;> }> // This code is contributed by Veerendra_Singh_Rajpoot> |
>
>
Java
import> java.util.*;> // Definition of a binary tree node> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> item)> >{> >data = item;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> class> Main {> >// Function to build a hash table or a map of parent> >// pointers for each node in the tree> >static> Map buildParentMap(Node root)> >{> >Map parentMap =>new> HashMap();> >parentMap.put(root,>null>);> >Queue queue =>new> LinkedList();> >queue.add(root);> >while> (!queue.isEmpty()) {> >Node node = queue.poll();> >if> (node.left !=>null>) {> >parentMap.put(node.left, node);> >queue.add(node.left);> >}> >if> (node.right !=>null>) {> >parentMap.put(node.right, node);> >queue.add(node.right);> >}> >}> >return> parentMap;> >}> >// Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two> >// nodes using an auxiliary data structure> >static> int> findLCA(Node root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >// Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers> >// for each node in the tree> >Map parentMap = buildParentMap(root);> >// Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> >Node p =>null>, q =>null>;> >Queue queue =>new> LinkedList();> >queue.add(root);> >while> (!queue.isEmpty()) {> >Node node = queue.poll();> >if> (node.data == n1) {> >p = node;> >}> >if> (node.data == n2) {> >q = node;> >}> >if> (node.left !=>null>) {> >queue.add(node.left);> >}> >if> (node.right !=>null>) {> >queue.add(node.right);> >}> >}> >// Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set> >// or a list> >Set ancestors =>new> HashSet();> >while> (p !=>null>) {> >ancestors.add(p);> >p = parentMap.get(p);> >}> >// Traverse up from the second node and check if> >// each ancestor is already in the set or the list> >while> (q !=>null>) {> >if> (ancestors.contains(q)) {> >return> q.data;> >}> >q = parentMap.get(q);> >}> >return> ->1>;>// No common ancestor found> >}> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >Node root =>new> Node(>1>);> >root.left =>new> Node(>2>);> >root.right =>new> Node(>3>);> >root.left.left =>new> Node(>4>);> >root.left.right =>new> Node(>5>);> >root.right.left =>new> Node(>6>);> >root.right.right =>new> Node(>7>);> >System.out.println(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> >+ findLCA(root,>4>,>5>));> >System.out.println(>'LCA(4, 6) = '> >+ findLCA(root,>4>,>6>));> >System.out.println(>'LCA(3, 4) = '> >+ findLCA(root,>3>,>4>));> >System.out.println(>'LCA(3, 4) = '> >+ findLCA(root,>2>,>4>));> >}> }> |
>
>
Python3
from> collections>import> deque> # Definition of a binary tree node> class> Node:> >def> __init__(>self>, data):> >self>.data>=> data> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> # Function to build a hash table or a map of parent> # pointers for each node in the tree> def> buildParentMap(root):> >parentMap>=> {}> >parentMap[root]>=> None> >queue>=> deque([root])> >while> queue:> >node>=> queue.popleft()> >if> node.left:> >parentMap[node.left]>=> node> >queue.append(node.left)> >if> node.right:> >parentMap[node.right]>=> node> >queue.append(node.right)> >return> parentMap> # Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two nodes> # using an auxiliary data structure> def> findLCA(root, n1, n2):> ># Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers for> ># each node in the tree> >parentMap>=> buildParentMap(root)> ># Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> >p, q>=> None>,>None> >queue>=> deque([root])> >while> queue:> >node>=> queue.popleft()> >if> node.data>=>=> n1:> >p>=> node> >if> node.data>=>=> n2:> >q>=> node> >if> node.left:> >queue.append(node.left)> >if> node.right:> >queue.append(node.right)> ># Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set or a> ># list> >ancestors>=> set>()> >while> p:> >ancestors.add(p)> >p>=> parentMap[p]> ># Traverse up from the second node and check if each> ># ancestor is already in the set or the list> >while> q:> >if> q>in> ancestors:> >return> q.data> >q>=> parentMap[q]> >return> ->1> # No common ancestor found> # Driver code> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> >root>=> Node(>1>)> >root.left>=> Node(>2>)> >root.right>=> Node(>3>)> >root.left.left>=> Node(>4>)> >root.left.right>=> Node(>5>)> >root.right.left>=> Node(>6>)> >root.right.right>=> Node(>7>)> >print>(>'LCA(4, 5) = '>, findLCA(root,>4>,>5>))> >print>(>'LCA(4, 6) = '>, findLCA(root,>4>,>6>))> >print>(>'LCA(3, 4) = '>, findLCA(root,>3>,>4>))> >print>(>'LCA(2, 4) = '>, findLCA(root,>2>,>4>))> |
>
>
C#
using> System;> using> System.Collections.Generic;> // Definition of a binary tree node> class> Node> {> >public> int> data;> >public> Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> item)> >{> >data = item;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> class> MainClass> {> >// Function to build a hash table or a map of parent> >// pointers for each node in the tree> >static> Dictionary BuildParentMap(Node root)> >{> >Dictionary parentMap =>new> Dictionary();> >parentMap.Add(root,>null>);> >Queue queue =>new> Queue();> >queue.Enqueue(root);> >while> (queue.Count != 0)> >{> >Node node = queue.Dequeue();> >if> (node.left !=>null>)> >{> >parentMap.Add(node.left, node);> >queue.Enqueue(node.left);> >}> >if> (node.right !=>null>)> >{> >parentMap.Add(node.right, node);> >queue.Enqueue(node.right);> >}> >}> >return> parentMap;> >}> >// Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two> >// nodes using an auxiliary data structure> >static> int> FindLCA(Node root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >// Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers> >// for each node in the tree> >Dictionary parentMap = BuildParentMap(root);> >// Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> >Node p =>null>, q =>null>;> >Queue queue =>new> Queue();> >queue.Enqueue(root);> >while> (queue.Count != 0)> >{> >Node node = queue.Dequeue();> >if> (node.data == n1)> >{> >p = node;> >}> >if> (node.data == n2)> >{> >q = node;> >}> >if> (node.left !=>null>)> >{> >queue.Enqueue(node.left);> >}> >if> (node.right !=>null>)> >{> >queue.Enqueue(node.right);> >}> >}> >// Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set> >// or a list> >HashSet ancestors =>new> HashSet();> >while> (p !=>null>)> >{> >ancestors.Add(p);> >p = parentMap[p];> >}> >// Traverse up from the second node and check if> >// each ancestor is already in the set or the list> >while> (q !=>null>)> >{> >if> (ancestors.Contains(q))> >{> >return> q.data;> >}> >q = parentMap[q];> >}> >return> -1;>// No common ancestor found> >}> >public> static> void> Main()> >{> >Node root =>new> Node(1);> >root.left =>new> Node(2);> >root.right =>new> Node(3);> >root.left.left =>new> Node(4);> >root.left.right =>new> Node(5);> >root.right.left =>new> Node(6);> >root.right.right =>new> Node(7);> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> + FindLCA(root, 4, 5));> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(4, 6) = '> + FindLCA(root, 4, 6));> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(3, 4) = '> + FindLCA(root, 3, 4));> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(2, 4) = '> + FindLCA(root, 2, 4));> >}> }> // This code is contributed by akashish__> |
>
>
Javascript
// javascript code addition> // Definition of a binary tree node> class Node {> >constructor(item) {> >this>.data = item;> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >}> }> // Function to build a hash table or a map of parent> // pointers for each node in the tree> function> buildParentMap(root) {> >const parentMap =>new> Map();> >parentMap.set(root,>null>);> >const queue = [];> >queue.push(root);> >while> (queue.length>0) {> >const node = queue.shift();> >if> (node.left !=>null>) {> >parentMap.set(node.left, node);> >queue.push(node.left);> >}> >if> (node.right !=>null>) {> >parentMap.set(node.right, node);> >queue.push(node.right);> >}> >}> >return> parentMap;> }> // Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two> // nodes using an auxiliary data structure> function> findLCA(root, n1, n2) {> >// Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers> >// for each node in the tree> >const parentMap = buildParentMap(root);> >// Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> >let p =>null>, q =>null>;> >const queue = [];> >queue.push(root);> >while> (queue.length>0) {> >const node = queue.shift();> >if> (node.data === n1) {> >p = node;> >}> >if> (node.data === n2) {> >q = node;> >}> >if> (node.left !=>null>) {> >queue.push(node.left);> >}> >if> (node.right !=>null>) {> >queue.push(node.right);> >}> >}> >// Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set> >// or a list> >const ancestors =>new> Set();> >while> (p !=>null>) {> >ancestors.add(p);> >p = parentMap.get(p);> >}> >// Traverse up from the second node and check if> >// each ancestor is already in the set or the list> >while> (q !=>null>) {> >if> (ancestors.has(q)) {> >return> q.data;> >}> >q = parentMap.get(q);> >}> >return> -1;>// No common ancestor found> }> // Test the function> const root =>new> Node(1);> root.left =>new> Node(2);> root.right =>new> Node(3);> root.left.left =>new> Node(4);> root.left.right =>new> Node(5);> root.right.left =>new> Node(6);> root.right.right =>new> Node(7);> console.log(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> + findLCA(root, 4, 5));> console.log(>'LCA(4, 6) = '> + findLCA(root, 4, 6));> console.log(>'LCA(3, 4) = '> + findLCA(root, 3, 4));> console.log(>'LCA(2, 4) = '> + findLCA(root, 2, 4));> // The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.> |
>
>Uitvoer
LCA(4, 5) = 2 LCA(4, 6) = 1 LCA(3,4) = 1 LCA(2, 4) = 2>
Tijdcomplexiteit: O(n),
typoscript datumtype
De tijdscomplexiteit van de gegeven code is O(n), waarbij n het aantal knooppunten in de binaire boom is.
Voor het bouwen van de bovenliggende kaart voor elk knooppunt in de boom moet elk knooppunt één keer worden bezocht, wat O(n) tijd kost. Om de knooppunten met de waarden n1 en n2 te vinden, moet elk knooppunt één keer worden bezocht, wat ook O(n) tijd kost. Het omhoog gaan vanaf het tweede knooppunt en controleren of elke voorouder al in de set of de lijst zit, kost O(h) tijd, waarbij h de hoogte van de binaire boom is.
In het ergste geval is de hoogte van de binaire boom O(n), als de binaire boom scheef staat. Daarom is de totale tijdscomplexiteit van de gegeven code O(n) + O(n) + O(n) = O(n).
Ruimtecomplexiteit: O(n),
De ruimtecomplexiteit van de gegeven code is in het ergste geval O(n). Dit komt omdat de grootte van de bovenliggende kaart die voor elk knooppunt in de boom is gebouwd, O(n) is. Bovendien kan de reeks voorouders in het ergste geval ook alle knooppunten in de binaire boom bevatten, wat ook O(n)-ruimte in beslag neemt. Ten slotte neemt de wachtrij die wordt gebruikt voor het doorlopen van de binaire boom O(n) ruimte in beslag. Daarom is de algehele ruimtecomplexiteit van de gegeven code O(n) + O(n) + O(n) = O(n).
We hebben een efficiënte oplossing besproken om LCA te vinden in de binaire zoekboom. In Binary Search Tree kunnen we, met behulp van BST-eigenschappen, LCA vinden in O(h) tijd waarbij h de hoogte van de boom is. Een dergelijke implementatie is niet mogelijk in Binary Tree, omdat de knooppunten van de Binary Tree-sleutels geen enkele volgorde volgen.
Misschien vindt u de onderstaande artikelen ook leuk:
LCA met behulp van Parent Pointer
Laagste gemeenschappelijke voorouder in een binaire zoekboom.
Zoek LCA in binaire structuur met behulp van RMQ
