De Java schakel verklaring voert één instructie uit meerdere voorwaarden uit. Het is als als-anders-als ladder verklaring. De switch-instructie werkt met byte, short, int, long, enum-typen, String en enkele wrapper-typen zoals Byte, Short, Int en Long. Sinds Java 7 kunt u snaren in de switch-instructie.
Met andere woorden: de switch-instructie test de gelijkheid van een variabele aan de hand van meerdere waarden.
Punten om te onthouden
- Er kan zijn één of N aantal casuswaarden voor een schakelexpressie.
- De case-waarde mag alleen van het type switch-expressie zijn. De casuswaarde moet zijn letterlijk of constant . Het staat niet toe variabelen .
- De hoofdletterwaarden moeten zijn uniek . In het geval van een dubbele waarde wordt er een compileerfout gegenereerd.
- De Java-switch-expressie moet van zijn byte, short, int, long (met zijn Wrapper-type), opsommingen en touwtje .
- Elke casusverklaring kan een verklaring breken wat optioneel is. Wanneer de controle reikt tot de verklaring breken , springt het naar het besturingselement na de switch-expressie. Als er geen break-instructie wordt gevonden, wordt de volgende case uitgevoerd.
- De casuswaarde kan een hebben standaardlabel wat optioneel is.
Syntaxis:
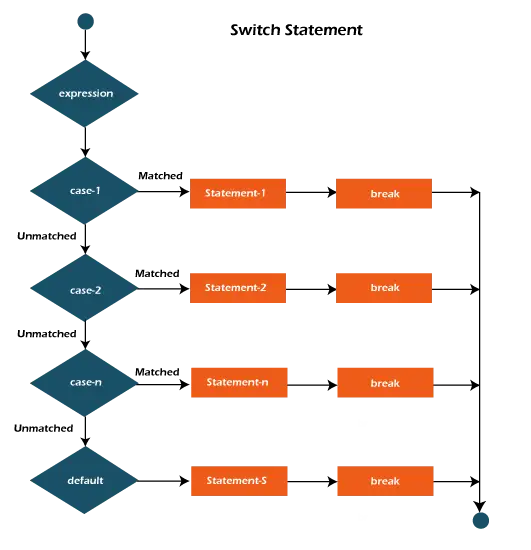
switch(expression){ case value1: //code to be executed; break; //optional case value2: //code to be executed; break; //optional ...... default: code to be executed if all cases are not matched; } Stroomdiagram van de Switch-verklaring
java-char naar geheel getal
Voorbeeld:
SwitchExample.java
public class SwitchExample { public static void main(String[] args) { //Declaring a variable for switch expression int number=20; //Switch expression switch(number){ //Case statements case 10: System.out.println('10'); break; case 20: System.out.println('20'); break; case 30: System.out.println('30'); break; //Default case statement default:System.out.println('Not in 10, 20 or 30'); } } } Test het nu Uitgang:
20
Voorbeeld van maand zoeken:
SwitchMonthExample.javaHTML
//Java Program to demonstrate the example of Switch statement //where we are printing month name for the given number public class SwitchMonthExample { public static void main(String[] args) { //Specifying month number int month=7; String monthString=''; //Switch statement switch(month){ //case statements within the switch block case 1: monthString='1 - January'; break; case 2: monthString='2 - February'; break; case 3: monthString='3 - March'; break; case 4: monthString='4 - April'; break; case 5: monthString='5 - May'; break; case 6: monthString='6 - June'; break; case 7: monthString='7 - July'; break; case 8: monthString='8 - August'; break; case 9: monthString='9 - September'; break; case 10: monthString='10 - October'; break; case 11: monthString='11 - November'; break; case 12: monthString='12 - December'; break; default:System.out.println('Invalid Month!'); } //Printing month of the given number System.out.println(monthString); } } Test het nu Uitgang:
7 - July
Programma om klinker of medeklinker te controleren:
Als het karakter A, E, I, O of U is, is het een klinker die anderszins consonant is. Het is niet hoofdlettergevoelig.
java voor lustypen
SwitchVowelExample.java
public class SwitchVowelExample { public static void main(String[] args) { char ch='O'; switch(ch) { case 'a': System.out.println('Vowel'); break; case 'e': System.out.println('Vowel'); break; case 'i': System.out.println('Vowel'); break; case 'o': System.out.println('Vowel'); break; case 'u': System.out.println('Vowel'); break; case 'A': System.out.println('Vowel'); break; case 'E': System.out.println('Vowel'); break; case 'I': System.out.println('Vowel'); break; case 'O': System.out.println('Vowel'); break; case 'U': System.out.println('Vowel'); break; default: System.out.println('Consonant'); } } } Uitgang:
Vowel
De Java Switch-verklaring is een fall-through
De Java-switch-instructie is een fall-through. Het betekent dat het alle instructies uitvoert na de eerste match als er geen break-instructie aanwezig is.
Voorbeeld:
Java-index van
Schakelvoorbeeld2.java
//Java Switch Example where we are omitting the //break statement public class SwitchExample2 { public static void main(String[] args) { int number=20; //switch expression with int value switch(number){ //switch cases without break statements case 10: System.out.println('10'); case 20: System.out.println('20'); case 30: System.out.println('30'); default:System.out.println('Not in 10, 20 or 30'); } } } Test het nu Uitgang:
20 30 Not in 10, 20 or 30
Java Switch-instructie met string
Met Java kunnen we strings gebruiken in switch-expressie sinds Java SE 7. De case-instructie moet letterlijk string zijn.
Voorbeeld:
SwitchStringExample.java
abstracte methoden
//Java Program to demonstrate the use of Java Switch //statement with String public class SwitchStringExample { public static void main(String[] args) { //Declaring String variable String levelString='Expert'; int level=0; //Using String in Switch expression switch(levelString){ //Using String Literal in Switch case case 'Beginner': level=1; break; case 'Intermediate': level=2; break; case 'Expert': level=3; break; default: level=0; break; } System.out.println('Your Level is: '+level); } } Test het nu Uitgang:
Your Level is: 3
Java Nested Switch-verklaring
We kunnen de switch-instructie gebruiken in een andere switch-instructie in Java. Het staat bekend als geneste switch-instructie.
Voorbeeld:
GenesteSwitchExample.java
//Java Program to demonstrate the use of Java Nested Switch public class NestedSwitchExample { public static void main(String args[]) { //C - CSE, E - ECE, M - Mechanical char branch = 'C'; int collegeYear = 4; switch( collegeYear ) { case 1: System.out.println('English, Maths, Science'); break; case 2: switch( branch ) { case 'C': System.out.println('Operating System, Java, Data Structure'); break; case 'E': System.out.println('Micro processors, Logic switching theory'); break; case 'M': System.out.println('Drawing, Manufacturing Machines'); break; } break; case 3: switch( branch ) { case 'C': System.out.println('Computer Organization, MultiMedia'); break; case 'E': System.out.println('Fundamentals of Logic Design, Microelectronics'); break; case 'M': System.out.println('Internal Combustion Engines, Mechanical Vibration'); break; } break; case 4: switch( branch ) { case 'C': System.out.println('Data Communication and Networks, MultiMedia'); break; case 'E': System.out.println('Embedded System, Image Processing'); break; case 'M': System.out.println('Production Technology, Thermal Engineering'); break; } break; } } } Test het nu Uitgang:
bevat in tekenreeks
Data Communication and Networks, MultiMedia
Java Enum in Switch-instructie
Met Java kunnen we enum gebruiken in de switch-instructie. Java-enum is een klasse die de groep constanten vertegenwoordigt. (onveranderlijk zoals eindvariabelen). We gebruiken het trefwoord enum en plaatsen de constanten tussen accolades, gescheiden door een komma.
Voorbeeld:
JavaSwitchEnumExample.java
//Java Program to demonstrate the use of Enum //in switch statement public class JavaSwitchEnumExample { public enum Day { Sun, Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat } public static void main(String args[]) { Day[] DayNow = Day.values(); for (Day Now : DayNow) { switch (Now) { case Sun: System.out.println('Sunday'); break; case Mon: System.out.println('Monday'); break; case Tue: System.out.println('Tuesday'); break; case Wed: System.out.println('Wednesday'); break; case Thu: System.out.println('Thursday'); break; case Fri: System.out.println('Friday'); break; case Sat: System.out.println('Saturday'); break; } } } } Test het nu Uitgang:
Sunday Monday Twesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday
Java-wrapper in Switch-instructie
Met Java kunnen we er vier gebruiken wrap klassen : Byte, Short, Integer en Long in switch-instructie.
Voorbeeld:
WrapperInSwitchCaseExample.java
//Java Program to demonstrate the use of Wrapper class //in switch statement public class WrapperInSwitchCaseExample { public static void main(String args[]) { Integer age = 18; switch (age) { case (16): System.out.println('You are under 18.'); break; case (18): System.out.println('You are eligible for vote.'); break; case (65): System.out.println('You are senior citizen.'); break; default: System.out.println('Please give the valid age.'); break; } } } Test het nu Uitgang:
You are eligible for vote.
