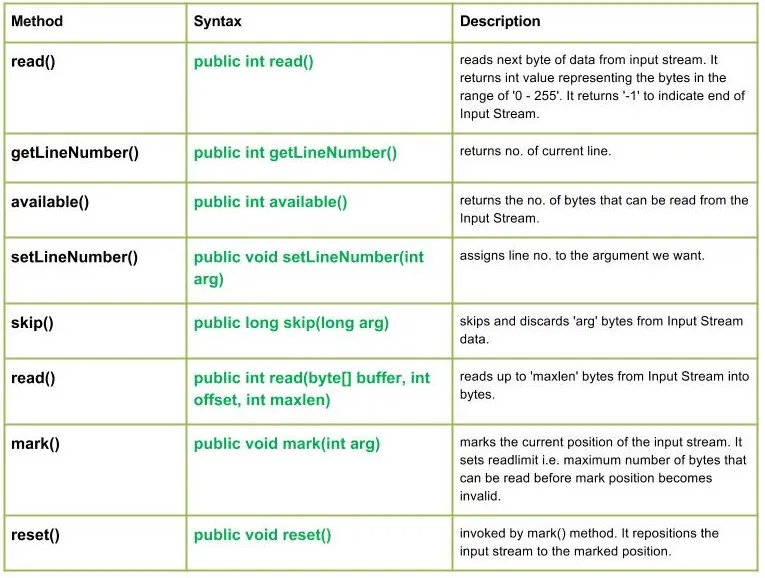
De klasse java.io.LineNumberInputStream is eenvoudigweg een uitbreiding van de invoerstroom en biedt een extra mogelijkheid om het huidige regelnummer bij te houden.
alfa-bèta-snoeien
Lijn is een reeks bytes die eindigt met: 'r', d.w.z. een Carriage Return-teken of een newline-teken: 'n' of een linefeed-teken dat volgt op het Carriage Return-teken.
Verklaring:
public class LineNumberInputStream extends Reader
Constructeurs:
LineNumberInputStream(InputStream in) : Constructs a newline no. stream that reads it's input from the specified Input Stream.
Methoden:
Syntaxis:
public int read() Parameters : ------- Return : int value representing the bytes in the range of '0 - 255'. return -1 indicating end of Input Stream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Implementatie:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); // read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer // '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // Since read() method returns Integer value // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; System.out.print(c); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Opmerking :
De volgende Java-code kan hier niet worden uitgevoerd omdat we geen toegang hebben tot bestanden op de online IDE.
Kopieer het programma dus naar uw systeem en voer het daar uit.
Hoe te converteren van int naar string in Java
De ABC.txt bestand dat in het programma wordt gebruikt, bevat:
Hello Geeks. Explaining read() method
Uitgang:
Hello Geeks. Explaining read() method
Syntaxis:
public int getLineNumber() Parameters : ------- Return : no. of current line
Implementatie:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of getLineNumber() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try { char c; int a b; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // Use of getLineNumber() : to print line no. a = geekline.getLineNumber(); System.out.println(' At line : ' + a); System.out.print(c); } a = geekline.getLineNumber(); System.out.println(' at line: ' + a); } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Opmerking :
De volgende Java-code kan hier niet worden uitgevoerd omdat we geen toegang hebben tot bestanden op de online IDE.
Kopieer het programma dus naar uw systeem en voer het daar uit.
De ABC.txt bestand dat in het programma wordt gebruikt, bevat:
no. of lines
Uitgang:
At line : 0 n At line : 0 o At line : 0 . At line : 0 At line : 0 o At line : 0 f At line : 1 At line : 1 l At line : 1 i At line : 1 n At line : 1 e At line : 1 s at line: 1
Syntaxis:
public int available() Parameters : ------- Return : returns the no. of bytes that can be read from the Input Stream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Implementatie:
industrie en fabriekJava
// Java program illustrating the working of available() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a b; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // Use of available method : return no. of bytes that can be read a = geekline.available(); System.out.println(c + ' Bytes available : ' + a); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Opmerking :
De volgende Java-code kan hier niet worden uitgevoerd omdat we geen toegang hebben tot bestanden op de online IDE.
Kopieer het programma dus naar uw systeem en voer het daar uit.
De ABC.txt bestand dat in het programma wordt gebruikt, bevat:
available
Uitgang:
a Bytes available : 4 v Bytes available : 3 a Bytes available : 3 i Bytes available : 2 l Bytes available : 2 a Bytes available : 1 b Bytes available : 1 l Bytes available : 0 e Bytes available : 0
Syntaxis:
public void setLineNumber(int arg) Parameters : arg : line number to assign Return : void Exception: -----
Implementatie:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of setLineNumber() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a b = 0; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // Use of setLineNumber() : to set the line no. geekline.setLineNumber(100 + b); // getLineNumber() : returning the current line no. a = geekline.getLineNumber(); System.out.println(c + ' Line No. Set : ' + a); b++; } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Opmerking :
De volgende Java-code kan hier niet worden uitgevoerd omdat we geen toegang hebben tot bestanden op de online IDE.
Kopieer het programma dus naar uw systeem en voer het daar uit.
De ABC.txt bestand dat in het programma wordt gebruikt, bevat:
LineNumber
Uitgang:
mooiste glimlach
L Line No. Set : 100 i Line No. Set : 101 n Line No. Set : 102 e Line No. Set : 103 N Line No. Set : 104 u Line No. Set : 105 m Line No. Set : 106 b Line No. Set : 107 e Line No. Set : 108 r Line No. Set : 109
Syntaxis:
public long skip(long arg) Parameters : arg : no. of bytes of Input Stream data to skip. Return : no. of bytes to be skipped Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Implementatie:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of setLineNumber() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a b = 0; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // skip() : to skip and discard 'arg' bytes // Here skip() will skip and discard 3 bytes. geekline.skip(3); System.out.println(c); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally{ // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Opmerking :
De volgende Java-code kan hier niet worden uitgevoerd omdat we geen toegang hebben tot bestanden op de online IDE.
Kopieer het programma dus naar uw systeem en voer het daar uit.
De ABC.txt bestand dat in het programma wordt gebruikt, bevat:
Program Explaining Skip() method
Uitgang: '
P r E a n k ) t
Syntaxis:
public int read(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) Parameters : buffer : buffer whose data to read offset : starting offset of the data maxlen : max. no. of bytes to read Return : total no. of bytes else return -1 if End of Input Stream is identified Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Implementatie:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); // read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer // '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream while((a=geekline.read())!=-1) { // Since read() method returns Integer value // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; System.out.print(c); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Opmerking :
De volgende Java-code kan hier niet worden uitgevoerd omdat we geen toegang hebben tot bestanden op de online IDE.
Kopieer het programma dus naar uw systeem en voer het daar uit.
De ABC.txt bestand dat in het programma wordt gebruikt, bevat:
Read() method
wat de methode doet is offset = r en maxlen = 5... dus ---i.e. 3 offset en vervolgens 5 bytes, d.w.z. Read( en dan opnieuw offset dus -
Uitgang:
converteer tekenreeks naar geheel getal
The number of char read: 5 ---Read(--
Syntaxis:
public void mark(int arg) Parameters : arg : integer specifying the read limit of the input Stream Return : void
Syntaxis:
public void reset() Parameters : ---- Return : void Exception : -> IOException : If I/O error occurs.
Java-programma met uitleg over LineNumberInputStream Class-methoden: reset() en mark()
Java// Java program illustrating the working of LineNumberInputStream method // mark() and reset() import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geek = null; try{ geek = new FileInputStream('GEEKS.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geek); // read() method : reading and printing Characters one by one System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); // mark() : read limiting the 'geek' input stream geekline.mark(0); // skip() : it results in reading of 'e' in G'e'eeks geekline.skip(1); System.out.println('skip() method comes to play'); System.out.println('mark() method comes to play'); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); boolean check = geekline.markSupported(); if(geekline.markSupported()) { // reset() method : repositioning the stream to marked positions. geekline.reset(); System.out.println('reset() invoked'); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); } else { System.out.println('reset() method not supported.'); } System.out.println('geekline.markSupported() supported reset() : ' + check); } catch(Exception except) { // in case of I/O error except.printStackTrace(); } finally { // releasing the resources back to the GarbageCollector when closes if(geek != null) geek.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Opmerking :
Deze code werkt niet op online IDE, omdat een dergelijk bestand hier niet aanwezig is.
U kunt deze code op uw systeem uitvoeren om de werking te controleren.
ABC.txt bestand dat in de code wordt gebruikt, heeft
HelloGeeks
Uitgang:
Char : H Char : e Char : l skip() method comes to play mark() method comes to play Char : o Char : G Char : e reset() method not supported. geekline.markSupported() supported reset() : false