De Totient-functie Φ(n) van Euler voor een invoer n is het aantal getallen in {1, 2, 3, …, n-1} die relatief priem zijn voor n, dat wil zeggen de getallen waarvan de GCD (grootste gemene deler) met n is 1.
Voorbeelden:
Φ(1) = 1
ggd(1, 1) is 1
Φ(2) = 1
ggd(1, 2) is 1, maar ggd(2, 2) is 2.
Φ(3) = 2
ggd(1, 3) is 1 en ggd(2, 3) is 1
Φ(4) = 2
ggd(1, 4) is 1 en ggd(3, 4) is 1
Φ(5) = 4
ggd(1, 5) is 1, ggd(2, 5) is 1,
ggd(3, 5) is 1 en ggd(4, 5) is 1
Φ(6) = 2
ggd(1, 6) is 1 en ggd(5, 6) is 1,
Aanbevolen oefening Euler Totient-functie Probeer het!
Hoe bereken je Φ(n) voor een invoer n?
A eenvoudige oplossing is het doorlopen van alle getallen van 1 tot n-1 en het tellen van getallen met ggd met n als 1. Hieronder staat de implementatie van de eenvoudige methode om de Totient-functie van Euler te berekenen voor een invoergetal n.
// A simple C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // A simple java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by sunnusingh>Python3 # A simple Python3 program # to calculate Euler's # Totient Function # Function to return # gcd of a and b def gcd(a, b): if (a == 0): return b return gcd(b % a, a) # A simple method to evaluate # Euler Totient Function def phi(n): result = 1 for i in range(2, n): if (gcd(i, n) == 1): result+=1 return result # Driver Code for n in range(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') = ', phi(n), sep = '') # This code is contributed # by Smitha>C# // A simple C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void Main() { for (int n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal>Javascript >PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd($a, $b) { if ($a == 0) return $b; return gcd($b % $a, $a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function function phi($n) { $result = 1; for ($i = 2; $i <$n; $i++) if (gcd($i, $n) == 1) $result++; return $result; } // Driver Code for ($n = 1; $n <= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>C++ // A simple C++ program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function #include using namespace std; // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) cout << 'phi('< Uitvoer
phi(1) = 1 phi(2) = 1 phi(3) = 2 phi(4) = 2 phi(5) = 4 phi(6) = 2 phi(7) = 6 phi(8) = 4 phi( 9) = 6 phi(10) = 4
conversie van int naar string in Java
De bovenstaande code roept de ggd-functie O(n) keer aan. De tijdscomplexiteit van de ggd-functie is O(h), waarbij h het aantal cijfers is in een kleiner aantal van gegeven twee getallen. Daarom is er een bovengrens voor de tijd complexiteit van de bovenstaande oplossing is O(N^2 log N) [Hoe Φ er maximaal Log kan zijn10n cijfers in alle getallen van 1 tot n]
Hulpruimte: O(log N)
Hieronder staat een Betere oplossing . Het idee is gebaseerd op de productformule van Euler, die stelt dat de waarde van de totient-functies lager is dan de totale productprime-factoren p van n.
De formule zegt feitelijk dat de waarde van Φ(n) gelijk is aan n vermenigvuldigd bijproduct van (1 – 1/p) voor alle priemfactoren p van n. Bijvoorbeeld de waarde van Φ(6) = 6 * (1-1/2) * (1 – 1/3) = 2.
We kunnen alle priemfactoren vinden met behulp van het gebruikte idee dit na.
1) Initialiseren: resultaat = n
2) Voer een lus uit van 'p' = 2 tot sqrt(n), doe het volgende voor elke 'p'.
a) Als p n deelt, dan
Instellen: resultaat = resultaat * (1,0 - (1,0 / (float) p));
Verdeel alle voorkomens van p in n.
3) Resultaat retourneren
Hieronder vindt u de implementatie van de productformule van Euler.
// C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function using Euler's // product formula #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and for every prime factor p, // multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultaat -= resultaat / n; //Aangezien in de verzameling {1,2,...,n-1} alle getallen relatief priem zijn met n //als n een priemgetal is, retourneert (int)resultaat; } // Stuurprogrammacode int main() { int n; voor(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) <C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula #include int phi(int n) { float result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultaat -= resultaat / n; //Aangezien in de verzameling {1,2,...,n-1} alle getallen relatief priem zijn met n //als n een priemgetal is, retourneert (int)resultaat; } // Stuurprogramma om bovenstaande functie te testen int main() { int n; voor (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // Java program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n and for // every prime factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultaat -= resultaat / n; //Aangezien in de verzameling {1,2,...,n-1} alle getallen relatief priem zijn met n //als n een priemgetal is, retourneert (int)resultaat; } // Stuurprogramma om bovenstaande functie te testen public static void main(String args[]) { int n; voor (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.>Python3 # Python 3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function # using Euler's product formula def phi(n) : result = n # Initialize result as n # Consider all prime factors # of n and for every prime # factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1 / p) p = 2 while p * p<= n : # Check if p is a prime factor. if n % p == 0 : # If yes, then update n and result while n % p == 0 : n = n // p result = result * (1.0 - (1.0 / float(p))) p = p + 1 # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most one # such prime factor) if n>1 : resultaat -= resultaat // n #Aangezien in de verzameling {1,2,...,n-1} alle getallen relatief priem zijn met n #als n een priemgetal is return int(result) # Driver programma om bovenstaande functie te testen voor n in bereik(1, 11) : print('phi(', n, ') = ', phi(n)) # Deze code is # bijgedragen door Nikita Tiwari.>C# // C# program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1 / p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (float)(1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultaat -= resultaat / n; //Aangezien in de verzameling {1,2,...,n-1} alle getallen relatief priem zijn met n //als n een priemgetal is, retourneert (int)resultaat; } // Stuurprogrammacode public static void Main() { int n; voor (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi(n) { // Initialize result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultaat -= resultaat / n; //Aangezien in de verzameling {1,2,...,n-1} alle getallen relatief priem zijn met n //als n een priemgetal is return parseInt(result); } // Stuurprogrammacode voor (laat n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi($n) { // Initialize result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n /= $p; $result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / $p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $resultaat -= $resultaat / $n; //Aangezien in de verzameling {1,2,...,n-1} alle getallen relatief priem zijn met n //als n een priemgetal is return intval($result); } // Stuurprogrammacode voor ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>> Uitvoer
Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Tijdcomplexiteit: O(Φ n log n)
Hulpruimte: O(1)
Met de bovenstaande methode kunnen we drijvende-kommaberekeningen vermijden. Het idee is om alle priemfactoren en hun veelvouden te tellen en deze telling van n af te trekken om de totient-functiewaarde te krijgen (priemfactoren en veelvouden van priemfactoren hebben niet ggd als 1)
1) Initialiseer het resultaat als n
2) Beschouw elk getal 'p' (waarbij 'p' varieert van 2 tot Φ(n)).
Als p n deelt, doe dan het volgende
a) Trek alle veelvouden van p af van 1 tot n [alle veelvouden van p
zal ggd meer dan 1 hebben (minstens p) met n]
b) Werk n bij door deze herhaaldelijk te delen door p.
3) Als de gereduceerde n groter is dan 1, verwijder dan alle veelvouden
van n uit resultaat.
Hieronder ziet u de implementatie van het bovenstaande algoritme.
C++ // C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and subtract their multiples // from result for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultaat -= resultaat / n; resultaat retourneren; } // Stuurprogrammacode int main() { int n; voor(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) << endl; } return 0; } // This code is contributed by koulick_sadhu>C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include int phi(int n) { int result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultaat -= resultaat / n; resultaat retourneren; } // Stuurprogramma om bovenstaande functie te testen int main() { int n; voor (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // Java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultaat -= resultaat / n; resultaat retourneren; } // Stuurprogrammacode public static void main (String[] args) { int n; voor (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by ajit>Python3 # Python3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function def phi(n): # Initialize result as n result = n; # Consider all prime factors # of n and subtract their # multiples from result p = 2; while(p * p <= n): # Check if p is a # prime factor. if (n % p == 0): # If yes, then # update n and result while (n % p == 0): n = int(n / p); result -= int(result / p); p += 1; # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most # one such prime factor) if (n>1): resultaat -= int(resultaat / n); resultaat retourneren; # Stuurprogrammacode voor n binnen bereik(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') =', phi(n)); # Deze code is # bijgedragen door mits>C# // C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and // subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultaat -= resultaat / n; resultaat retourneren; } // Stuurprogrammacode statisch openbaar ongeldig Main () { int n; voor (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed // by akt_mit>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi(n) { // Initialize // result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while (n % p == 0) n = parseInt(n / p); result -= parseInt(result / p); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultaat -= parseInt(resultaat / n); resultaat retourneren; } // Stuurprogrammacode voor (laat n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed // by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi($n) { // Initialize // result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n = (int)$n / $p; $result -= (int)$result / $p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $resultaat -= (int)$resultaat / $n; retourneer $resultaat; } // Stuurprogrammacode voor ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(', $n,') =', phi($n), '
'; // This code is contributed // by ajit Φ>> Uitvoer
Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Tijdcomplexiteit: O(Φ n log n)
Hulpruimte: O(1)
Laten we een voorbeeld nemen om het bovenstaande algoritme te begrijpen.
muis scrollen werkt niet
n = 10.
Initialiseren: resultaat = 10
2 is een priemfactor, dus n = n/i = 5, resultaat = 5
3 is geen hoofdfactor.
De for-lus stopt na 3 als 4*4 is niet kleiner dan of gelijk
tot 10.
Na for-lus, resultaat = 5, n = 5
Omdat n> 1, resultaat = resultaat - resultaat/n = 4
Enkele interessante eigenschappen van de totient-functie van Euler
1) Voor een priemgetal blz ,
Bewijs :
Voorbeelden:
mac-besturingssystemen
2) Voor twee priemgetallen a en b
Bewijs :
Voorbeelden:
3) Voor een priemgetal blz ,
C#-codevoorbeelden
Bewijs :
Voorbeelden:
4) Voor twee nummer a en b
Speciaal geval: ggd(a, b) = 1
Voorbeelden:
Speciaal geval :
5) De som van de waarden van totient-functies van alle delers van n is gelijk aan n.
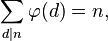
Voorbeelden:
n = 6
factoren = {1, 2, 3, 6}
n =
het alfabet nummeren
6) Het bekendste en belangrijkste kenmerk komt tot uiting in De stelling van Euler :
De stelling stelt dat als n en a coprime zijn
(of relatief priemgetal) positieve gehele getallen dus
AΦ(n)Φ 1 (mod n)
De RSA cryptosysteem is gebaseerd op deze stelling:
In het specifieke geval waarin m een priemgetal is, bijvoorbeeld p, verandert de stelling van Euler in de zogenaamde De kleine stelling van Fermat :
Ap-1Φ 1 (tegen p)
7) Aantal generatoren van een eindige cyclische groep onder modulo n-optelling is Φ(n) .
Gerelateerd artikel:
Euler's Totient-functie voor alle getallen kleiner dan of gelijk aan n
Geoptimaliseerde Euler Totient-functie voor meerdere evaluaties
Referenties:
http://e-maxx.ru/algo/euler_function
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_totient_function
https://cp-algorithms.com/algebra/phi-function.html
http://mathcenter.oxford.memory.edu/site/math125/chineseRemainderTheorem/
