De opsomming in C wordt ook wel het opgesomde type genoemd. Het is een door de gebruiker gedefinieerd gegevenstype dat bestaat uit gehele waarden, en dat betekenisvolle namen aan deze waarden geeft. Het gebruik van enum in C maakt het programma gemakkelijk te begrijpen en te onderhouden. De enum wordt gedefinieerd met behulp van het sleutelwoord enum.
Dit is de manier om de enum in C te definiëren:
enum flag{integer_const1, integer_const2,.....integter_constN}; In de bovenstaande declaratie definiëren we de enum met de naam vlag die 'N' gehele constanten bevat. De standaardwaarde van integer_const1 is 0, integer_const2 is 1, enzovoort. We kunnen ook de standaardwaarde van de gehele constanten wijzigen op het moment van de declaratie.
Bijvoorbeeld:
enum fruits{mango, apple, strawberry, papaya}; De standaardwaarde van mango is 0, appel is 1, aardbei is 2 en papaja is 3. Als we deze standaardwaarden willen wijzigen, kunnen we het volgende doen:
enum fruits{ mango=2, apple=1, strawberry=5, papaya=7, }; Opgesomde typeverklaring
Zoals we weten, moeten we in de C-taal de variabele van een vooraf gedefinieerd type declareren, zoals int, float, char, enz. Op dezelfde manier kunnen we de variabele declareren van een door de gebruiker gedefinieerd gegevenstype, zoals enum. Laten we eens kijken hoe we de variabele van een enum-type kunnen declareren.
Stel dat we de enum van typestatus maken, zoals hieronder weergegeven:
enum status{false,true}; Nu maken we de variabele van het statustype:
enum status s; // creating a variable of the status type.
In de bovenstaande verklaring hebben we de 's'-variabele van het type status gedeclareerd.
Om een variabele te maken, kunnen de bovenstaande twee uitspraken als volgt worden geschreven:
enum status{false,true} s; In dit geval is de standaardwaarde false gelijk aan 0 en de waarde true gelijk aan 1.
Laten we een eenvoudig programma van enum maken.
#include enum weekdays{Sunday=1, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday}; int main() { enum weekdays w; // variable declaration of weekdays type w=Monday; // assigning value of Monday to w. printf('The value of w is %d',w); return 0; } In de bovenstaande code maken we een enumtype met de naam weekdagen, en dit bevat de naam van alle zeven dagen. We hebben 1 waarde aan de zondag toegekend, en alle andere namen krijgen een waarde zoals de vorige waarde plus één.
Uitvoer
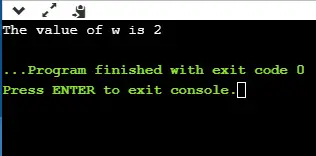
Laten we nog een voorbeeld demonstreren om de enum duidelijker te begrijpen.
#include enum months{jan=1, feb, march, april, may, june, july, august, september, october, november, december}; int main() { // printing the values of months for(int i=jan;i<=december;i++) { printf('%d, ',i); } return 0; < pre> <p>In the above code, we have created a type of enum named as months which consists of all the names of months. We have assigned a '1' value, and all the other months will be given a value as the previous one plus one. Inside the main() method, we have defined a for loop in which we initialize the 'i' variable by jan, and this loop will iterate till December.</p> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-2.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <h3>Why do we use enum?</h3> <p>The enum is used when we want our variable to have only a set of values. For example, we create a direction variable. As we know that four directions exist (North, South, East, West), so this direction variable will have four possible values. But the variable can hold only one value at a time. If we try to provide some different value to this variable, then it will throw the compilation error.</p> <p>The enum is also used in a switch case statement in which we pass the enum variable in a switch parenthesis. It ensures that the value of the case block should be defined in an enum.</p> <p> <strong>Let's see how we can use an enum in a switch case statement.</strong> </p> <pre> #include enum days{sunday=1, monday, tuesday, wednesday, thursday, friday, saturday}; int main() { enum days d; d=monday; switch(d) { case sunday: printf('Today is sunday'); break; case monday: printf('Today is monday'); break; case tuesday: printf('Today is tuesday'); break; case wednesday: printf('Today is wednesday'); break; case thursday: printf('Today is thursday'); break; case friday: printf('Today is friday'); break; case saturday: printf('Today is saturday'); break; } return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-3.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <p> <strong>Some important points related to enum</strong> </p> <ul> <li>The enum names available in an enum type can have the same value. Let's look at the example.</li> </ul> <pre> #include int main(void) { enum fruits{mango = 1, strawberry=0, apple=1}; printf('The value of mango is %d', mango); printf('
The value of apple is %d', apple); return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-4.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <ul> <li>If we do not provide any value to the enum names, then the compiler will automatically assign the default values to the enum names starting from 0.</li> <li>We can also provide the values to the enum name in any order, and the unassigned names will get the default value as the previous one plus one.</li> <li>The values assigned to the enum names must be integral constant, i.e., it should not be of other types such string, float, etc.</li> <li>All the enum names must be unique in their scope, i.e., if we define two enum having same scope, then these two enums should have different enum names otherwise compiler will throw an error.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Let's understand this scenario through an example.</strong> </p> <pre> #include enum status{success, fail}; enum boolen{fail,pass}; int main(void) { printf('The value of success is %d', success); return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-5.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <ul> <li>In enumeration, we can define an enumerated data type without the name also.</li> </ul> <pre> #include enum {success, fail} status; int main(void) { status=success; printf('The value of status is %d', status); return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-6.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <h3>Enum vs. Macro in C</h3> <ul> <li>Macro can also be used to define the name constants, but in case of an enum, all the name constants can be grouped together in a single statement. <br> For example, <br> # define pass 0; <br> # define success 1; <br> The above two statements can be written in a single statement by using the enum type. <br> enum status{pass, success};</li> <li>The enum type follows the scope rules while macro does not follow the scope rules.</li> <li>In Enum, if we do not assign the values to the enum names, then the compiler will automatically assign the default value to the enum names. But, in the case of macro, the values need to be explicitly assigned.</li> <li>The type of enum in C is an integer, but the type of macro can be of any type.</li> </ul> <hr></=december;i++)> Uitvoer

Enkele belangrijke punten met betrekking tot enum
- De opsommingsnamen die beschikbaar zijn in een opsommingstype kunnen dezelfde waarde hebben. Laten we naar het voorbeeld kijken.
#include int main(void) { enum fruits{mango = 1, strawberry=0, apple=1}; printf('The value of mango is %d', mango); printf('
The value of apple is %d', apple); return 0; } Uitvoer

- Als we geen waarde aan de enumnamen opgeven, wijst de compiler automatisch de standaardwaarden toe aan de enumnamen, beginnend bij 0.
- We kunnen de waarden ook in willekeurige volgorde aan de enumnaam opgeven, en de niet-toegewezen namen krijgen de standaardwaarde als de vorige plus één.
- De waarden die aan de enum-namen worden toegewezen, moeten integraal constant zijn, dat wil zeggen dat ze niet van andere typen mogen zijn, zoals string, float, enz.
- Alle enum-namen moeten uniek zijn in hun bereik, dat wil zeggen: als we twee enums definiëren met hetzelfde bereik, dan moeten deze twee enums verschillende enum-namen hebben, anders zal de compiler een fout genereren.
Laten we dit scenario begrijpen aan de hand van een voorbeeld.
#include enum status{success, fail}; enum boolen{fail,pass}; int main(void) { printf('The value of success is %d', success); return 0; } Uitvoer

- Bij opsomming kunnen we een opgesomd gegevenstype ook zonder de naam definiëren.
#include enum {success, fail} status; int main(void) { status=success; printf('The value of status is %d', status); return 0; } Uitvoer

Enum versus macro in C
- Macro kan ook worden gebruikt om de naamconstanten te definiëren, maar in het geval van een enum kunnen alle naamconstanten in één enkele instructie worden gegroepeerd.
Bijvoorbeeld,
# definieer doorgang 0;
# definieer succes 1;
De bovenstaande twee instructies kunnen in één enkele instructie worden geschreven door het type enum te gebruiken.
enum status{pass, succes}; - Het enum-type volgt de bereikregels, terwijl de macro de bereikregels niet volgt.
- Als we in Enum de waarden niet aan de enum-namen toewijzen, zal de compiler automatisch de standaardwaarde aan de enum-namen toewijzen. Maar in het geval van een macro moeten de waarden expliciet worden toegewezen.
- Het type enum in C is een geheel getal, maar het type macro kan van elk type zijn.
