Het woord ' proberen ' is een fragment uit het woord ' ophalen '. Trie is een gesorteerde, op bomen gebaseerde datastructuur die de reeks strings opslaat. Het heeft een aantal verwijzingen dat gelijk is aan het aantal tekens van het alfabet in elk knooppunt. Het kan een woord in het woordenboek zoeken met behulp van het voorvoegsel van het woord. Als we bijvoorbeeld aannemen dat alle strings worden gevormd uit de letters ' A ' naar ' Met ' in het Engelse alfabet kan elk trie-knooppunt er maximaal zijn 26 punten.
bytes naar stringpython
Trie wordt ook wel de digitale boom of voorvoegselboom genoemd. De positie van een knooppunt in de Trie bepaalt de sleutel waarmee dat knooppunt is verbonden.
Eigenschappen van de Trie voor een set van de string:
- Het hoofdknooppunt van de trie vertegenwoordigt altijd het nulknooppunt.
- Elk kind van knooppunten wordt alfabetisch gesorteerd.
- Elk knooppunt kan maximaal 26 kinderen (A t/m Z).
- Elk knooppunt (behalve de wortel) kan één letter van het alfabet opslaan.
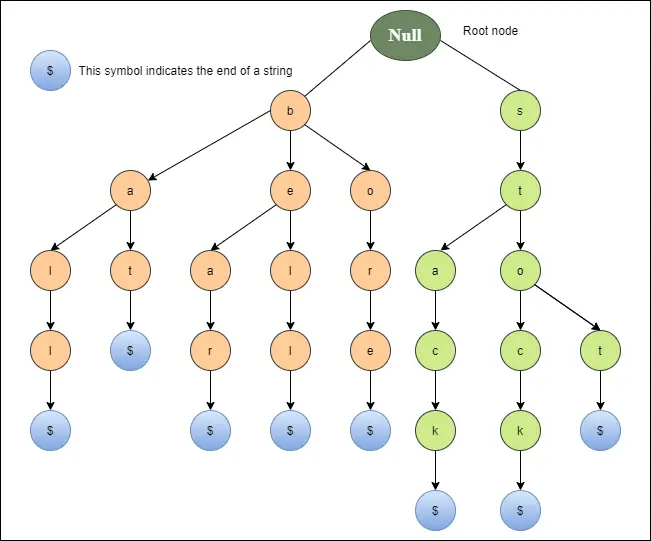
Het onderstaande diagram toont een drievoudige weergave voor de bel, beer, boring, knuppel, bal, stop, kolf en stapel.
Basisbewerkingen van Trie
Er zijn drie operaties in de Trie:
- Inbrengen van een knooppunt
- Een knooppunt zoeken
- Verwijdering van een knooppunt
Invoegen van een knooppunt in de Trie
De eerste bewerking is het invoegen van een nieuw knooppunt in de tri. Voordat we met de implementatie beginnen, is het belangrijk om enkele punten te begrijpen:
- Elke letter van de invoersleutel (woord) wordt als individu in de Trie_node ingevoegd. Merk op dat kinderen naar het volgende niveau van Trie-knooppunten wijzen.
- De sleutelkarakterarray fungeert als een index van kinderen.
- Als het huidige knooppunt al een verwijzing naar de huidige letter heeft, stelt u het huidige knooppunt in op dat knooppunt waarnaar wordt verwezen. Maak anders een nieuw knooppunt, stel de letter in op de huidige letter en begin zelfs het huidige knooppunt met dit nieuwe knooppunt.
- De karakterlengte bepaalt de diepte van de trie.
Implementatie van een nieuw knooppunt invoegen in de Trie
public class Data_Trie { private Node_Trie root; public Data_Trie(){ this.root = new Node_Trie(); } public void insert(String word){ Node_Trie current = root; int length = word.length(); for (int x = 0; x <length; x++){ char l="word.charAt(x);" node_trie node="current.getNode().get(L);" if (node="=" null){ (); current.getnode().put(l, node); } current="node;" current.setword(true); < pre> <h3>Searching a node in Trie</h3> <p>The second operation is to search for a node in a Trie. The searching operation is similar to the insertion operation. The search operation is used to search a key in the trie. The implementation of the searching operation is shown below.</p> <p>Implementation of search a node in the Trie</p> <pre> class Search_Trie { private Node_Trie Prefix_Search(String W) { Node_Trie node = R; for (int x = 0; x <w.length(); x++) { char curletter="W.charAt(x);" if (node.containskey(curletter)) node="node.get(curLetter);" } else return null; node; public boolean search(string w) node_trie !="null" && node.isend(); < pre> <h3>Deletion of a node in the Trie</h3> <p>The Third operation is the deletion of a node in the Trie. Before we begin the implementation, it is important to understand some points:</p> <ol class="points"> <li>If the key is not found in the trie, the delete operation will stop and exit it.</li> <li>If the key is found in the trie, delete it from the trie.</li> </ol> <p> <strong>Implementation of delete a node in the Trie</strong> </p> <pre> public void Node_delete(String W) { Node_delete(R, W, 0); } private boolean Node_delete(Node_Trie current, String W, int Node_index) { if (Node_index == W.length()) { if (!current.isEndOfWord()) { return false; } current.setEndOfWord(false); return current.getChildren().isEmpty(); } char A = W.charAt(Node_index); Node_Trie node = current.getChildren().get(A); if (node == null) { return false; } boolean Current_Node_Delete = Node_delete(node, W, Node_index + 1) && !node.isEndOfWord(); if (Current_Node_Delete) { current.getChildren().remove(A); return current.getChildren().isEmpty(); } return false; } </pre> <h2>Applications of Trie</h2> <p> <strong>1. Spell Checker</strong> </p> <p>Spell checking is a three-step process. First, look for that word in a dictionary, generate possible suggestions, and then sort the suggestion words with the desired word at the top.</p> <p>Trie is used to store the word in dictionaries. The spell checker can easily be applied in the most efficient way by searching for words on a data structure. Using trie not only makes it easy to see the word in the dictionary, but it is also simple to build an algorithm to include a collection of relevant words or suggestions.</p> <p> <strong>2. Auto-complete</strong> </p> <p>Auto-complete functionality is widely used on text editors, mobile applications, and the Internet. It provides a simple way to find an alternative word to complete the word for the following reasons.</p> <ul> <li>It provides an alphabetical filter of entries by the key of the node.</li> <li>We trace pointers only to get the node that represents the string entered by the user.</li> <li>As soon as you start typing, it tries to complete your input.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>3. Browser history</strong> </p> <p>It is also used to complete the URL in the browser. The browser keeps a history of the URLs of the websites you've visited.</p> <h2>Advantages of Trie</h2> <ol class="points"> <li>It can be insert faster and search the string than hash tables and binary search trees.</li> <li>It provides an alphabetical filter of entries by the key of the node.</li> </ol> <h2>Disadvantages of Trie</h2> <ol class="points"> <li>It requires more memory to store the strings.</li> <li>It is slower than the hash table.</li> </ol> <h2>Complete program in C++</h2> <pre> #include #include #include #define N 26 typedef struct TrieNode TrieNode; struct TrieNode { char info; TrieNode* child[N]; int data; }; TrieNode* trie_make(char info) { TrieNode* node = (TrieNode*) calloc (1, sizeof(TrieNode)); for (int i = 0; i <n; i++) node → child[i]="NULL;" data="0;" info="info;" return node; } void free_trienode(trienode* node) { for(int i="0;" < n; if (node !="NULL)" free_trienode(node child[i]); else continue; free(node); trie loop start trienode* trie_insert(trienode* flag, char* word) temp="flag;" for (int word[i] ; int idx="(int)" - 'a'; (temp child[idx]="=" null) child[idx]; }trie flag; search_trie(trienode* position="word[i]" child[position]="=" 0; child[position]; && 1) 1; check_divergence(trienode* len="strlen(word);" (len="=" 0) last_index="0;" len; child[position]) j="0;" <n; j++) (j child[j]) + break; last_index; find_longest_prefix(trienode* (!word || word[0]="=" '�') null; longest_prefix="(char*)" calloc 1, sizeof(char)); longest_prefix[i]="word[i];" longest_prefix[len]="�" branch_idx="check_divergence(flag," longest_prefix) (branch_idx>= 0) { longest_prefix[branch_idx] = '�'; longest_prefix = (char*) realloc (longest_prefix, (branch_idx + 1) * sizeof(char)); } return longest_prefix; } int data_node(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { TrieNode* temp = flag; for (int i = 0; word[i]; i++) { int position = (int) word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) { temp = temp → child[position]; } } return temp → data; } TrieNode* trie_delete(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { if (!flag) return NULL; if (!word || word[0] == '�') return flag; if (!data_node(flag, word)) { return flag; } TrieNode* temp = flag; char* longest_prefix = find_longest_prefix(flag, word); if (longest_prefix[0] == '�') { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } int i; for (i = 0; longest_prefix[i] != '�'; i++) { int position = (int) longest_prefix[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position] != NULL) { temp = temp → child[position]; } else { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } } int len = strlen(word); for (; i <len; i++) { int position="(int)" word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) trienode* rm_node="temp→child[position];" temp child[position]="NULL;" free_trienode(rm_node); } free(longest_prefix); return flag; void print_trie(trienode* flag) (!flag) return; printf('%c ', temp→info); for (int i="0;" < n; print_trie(temp child[i]); search(trienode* flag, char* word) printf('search the word %s: word); (search_trie(flag, 0) printf('not found
'); else printf('found!
'); main() flag="trie_make('�');" 'oh'); 'way'); 'bag'); 'can'); search(flag, 'ohh'); 'ways'); print_trie(flag); printf('
'); printf('deleting 'hello'...
'); 'can'...
'); free_trienode(flag); 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Search the word ohh: Not Found Search the word bag: Found! Search the word can: Found! Search the word ways: Not Found Search the word way: Found! → h → e → l → l → o → w → a → y → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'hello'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'can'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g </pre> <hr></len;></n;></pre></w.length();></pre></length;> Toepassingen van Trie
1. Spellingcontrole
Spellingcontrole bestaat uit drie stappen. Zoek eerst dat woord op in een woordenboek, genereer mogelijke suggesties en sorteer vervolgens de suggestiewoorden met het gewenste woord bovenaan.
een kaart herhalen in Java
Trie wordt gebruikt om het woord in woordenboeken op te slaan. De spellingcontrole kan eenvoudig en op de meest efficiënte manier worden toegepast door te zoeken naar woorden in een datastructuur. Het gebruik van trie maakt het niet alleen gemakkelijk om het woord in het woordenboek te zien, maar het is ook eenvoudig om een algoritme te bouwen dat een verzameling relevante woorden of suggesties opneemt.
latex lettergroottes
2. Automatisch aanvullen
De functionaliteit voor automatisch aanvullen wordt veel gebruikt in teksteditors, mobiele applicaties en internet. Het biedt een eenvoudige manier om een alternatief woord te vinden om het woord aan te vullen, om de volgende redenen.
- Het biedt een alfabetisch filter van vermeldingen op basis van de sleutel van het knooppunt.
- We traceren alleen pointers om het knooppunt te verkrijgen dat de door de gebruiker ingevoerde string vertegenwoordigt.
- Zodra u begint te typen, probeert het uw invoer te voltooien.
3. Browsergeschiedenis
Het wordt ook gebruikt om de URL in de browser aan te vullen. De browser houdt een geschiedenis bij van de URL's van de websites die u hebt bezocht.
Voordelen van Trie
- Het kan sneller worden ingevoegd en de string doorzoeken dan hashtabellen en binaire zoekbomen.
- Het biedt een alfabetisch filter van vermeldingen op basis van de sleutel van het knooppunt.
Nadelen van Trie
- Er is meer geheugen nodig om de strings op te slaan.
- Het is langzamer dan de hashtabel.
Compleet programma in C++
#include #include #include #define N 26 typedef struct TrieNode TrieNode; struct TrieNode { char info; TrieNode* child[N]; int data; }; TrieNode* trie_make(char info) { TrieNode* node = (TrieNode*) calloc (1, sizeof(TrieNode)); for (int i = 0; i <n; i++) node → child[i]="NULL;" data="0;" info="info;" return node; } void free_trienode(trienode* node) { for(int i="0;" < n; if (node !="NULL)" free_trienode(node child[i]); else continue; free(node); trie loop start trienode* trie_insert(trienode* flag, char* word) temp="flag;" for (int word[i] ; int idx="(int)" - \'a\'; (temp child[idx]="=" null) child[idx]; }trie flag; search_trie(trienode* position="word[i]" child[position]="=" 0; child[position]; && 1) 1; check_divergence(trienode* len="strlen(word);" (len="=" 0) last_index="0;" len; child[position]) j="0;" <n; j++) (j child[j]) + break; last_index; find_longest_prefix(trienode* (!word || word[0]="=" \'�\') null; longest_prefix="(char*)" calloc 1, sizeof(char)); longest_prefix[i]="word[i];" longest_prefix[len]="�" branch_idx="check_divergence(flag," longest_prefix) (branch_idx>= 0) { longest_prefix[branch_idx] = '�'; longest_prefix = (char*) realloc (longest_prefix, (branch_idx + 1) * sizeof(char)); } return longest_prefix; } int data_node(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { TrieNode* temp = flag; for (int i = 0; word[i]; i++) { int position = (int) word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) { temp = temp → child[position]; } } return temp → data; } TrieNode* trie_delete(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { if (!flag) return NULL; if (!word || word[0] == '�') return flag; if (!data_node(flag, word)) { return flag; } TrieNode* temp = flag; char* longest_prefix = find_longest_prefix(flag, word); if (longest_prefix[0] == '�') { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } int i; for (i = 0; longest_prefix[i] != '�'; i++) { int position = (int) longest_prefix[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position] != NULL) { temp = temp → child[position]; } else { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } } int len = strlen(word); for (; i <len; i++) { int position="(int)" word[i] - \'a\'; if (temp → child[position]) trienode* rm_node="temp→child[position];" temp child[position]="NULL;" free_trienode(rm_node); } free(longest_prefix); return flag; void print_trie(trienode* flag) (!flag) return; printf(\'%c \', temp→info); for (int i="0;" < n; print_trie(temp child[i]); search(trienode* flag, char* word) printf(\'search the word %s: word); (search_trie(flag, 0) printf(\'not found
\'); else printf(\'found!
\'); main() flag="trie_make('�');" \'oh\'); \'way\'); \'bag\'); \'can\'); search(flag, \'ohh\'); \'ways\'); print_trie(flag); printf(\'
\'); printf(\'deleting \'hello\'...
\'); \'can\'...
\'); free_trienode(flag); 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Search the word ohh: Not Found Search the word bag: Found! Search the word can: Found! Search the word ways: Not Found Search the word way: Found! → h → e → l → l → o → w → a → y → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'hello'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'can'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g </pre> <hr></len;></n;> 