ROT13-cijfer (lees als - 13 plaatsen roteren) is een speciaal geval van het Ceaser-cijfer waarin de verschuiving altijd 13 is.
Elke letter wordt dus 13 plaatsen verschoven om het bericht te coderen of te decoderen.
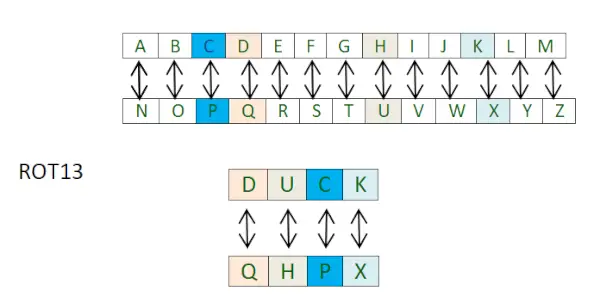
Je moet denken dat het gewoon weer een caesarcijfer is wat is er deze keer anders? Het verschil zit hem in de implementatie ervan. De aanpak is om twee afzonderlijke Python-woordenboeken te gebruiken.
- De eerste die de verschillende letters opzoekt op basis van hun plaats in het Engelse alfabet om het verschoven nummer te krijgen
- Tweede om de letters te krijgen die overeenkomen met die verschoven cijfers.
Implementatie:
C++
// CPP program to implement> // ROT13 Caesar Cipher> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Map to lookup the index of alphabets> map <>char>,>int>>dict1;> // Map to lookup alphabets corresponding> // to the index after shift> map <>int>,>char>>dict2;> // Function to create map to lookup> void> create_dict()> {> >for>(>int> i = 1; i <27; i++)> >dict1[>char>(64 + i)] = i;> > >dict2[0] =>'Z'>;> > >for>(>int> i = 1; i <26; i++)> >dict2[i] =>char>(64 + i);> > >return>;> }> // Function to encrypt the string> // according to the shift provided> string encrypt(string message,>int> shift)> {> >string cipher =>''>;> >for>(>int> i = 0; i { // Checking for namespace if(message[i] != ' ') { // looks up the map and // adds the shift to the index int num = (dict1[message[i]] + shift) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them cipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space cipher += ' '; } } return cipher; } // Function to decrypt the string // according to the shift provided string decrypt(string message, int shift) { string decipher = ''; for(int i = 0; i { // checks for space if(message[i] != ' ') { // looks up the map and // subtracts the shift to the index int num = (dict1[message[i]] - shift + 26) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them decipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space decipher += ' '; } } return decipher; } // Driver code int main() { create_dict(); string message = 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'; int shift = 13; cout << encrypt(message, shift) << '
'; message = 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'; shift = 13; cout << decrypt(message, shift) << '
'; return 0; } // This code is contributed by Sachin Bisht> |
document.queryselector
>
>
Java
// java program for the above approach> import> java.util.*;> public> class> Main {> >// Map to lookup the index of alphabets> >static> Map dict1 =>new> HashMap();> >// Map to lookup alphabets corresponding> >// to the index after shift> >static> Map dict2 =>new> HashMap();> >// Function to create map to lookup> >static> void> create_dict() {> >for>(>int> i =>1>; i <>27>; i++)> >dict1.put((>char>)(>64> + i), i);> >dict2.put(>0>,>'Z'>);> >for>(>int> i =>1>; i <>26>; i++)> >dict2.put(i, (>char>)(>64> + i));> >}> >// Function to encrypt the string> >// according to the shift provided> >static> String encrypt(String message,>int> shift) {> >String cipher =>''>;> >for>(>int> i =>0>; i // Checking for namespace if(message.charAt(i) != ' ') { // looks up the map and // adds the shift to the index int num = (dict1.get(message.charAt(i)) + shift) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them cipher += dict2.get(num); } else { // adds space cipher += ' '; } } return cipher; } // Function to decrypt the string // according to the shift provided static String decrypt(String message, int shift) { String decipher = ''; for(int i = 0; i // checks for space if(message.charAt(i) != ' ') { // looks up the map and // subtracts the shift to the index int num = (dict1.get(message.charAt(i)) - shift + 26) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them decipher += dict2.get(num); } else { // adds space decipher += ' '; } } return decipher; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { create_dict(); String message = 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'; int shift = 13; System.out.println(encrypt(message, shift)); message = 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'; shift = 13; System.out.println(decrypt(message, shift)); } } // This code is contributed by prince> |
>
>
Python3
obj in java
# Python program to implement> # ROT13 Caesar cipher> '''This script uses dictionaries instead of 'chr()' & 'ord()' function'''> # Dictionary to lookup the index of alphabets> dict1>=> {>'A'> :>1>,>'B'> :>2>,>'C'> :>3>,>'D'> :>4>,>'E'> :>5>,> >'F'> :>6>,>'G'> :>7>,>'H'> :>8>,>'I'> :>9>,>'J'> :>10>,> >'K'> :>11>,>'L'> :>12>,>'M'> :>13>,>'N'> :>14>,>'O'> :>15>,> >'P'> :>16>,>'Q'> :>17>,>'R'> :>18>,>'S'> :>19>,>'T'> :>20>,> >'U'> :>21>,>'V'> :>22>,>'W'> :>23>,>'X'> :>24>,>'Y'> :>25>,>'Z'> :>26>}> # Dictionary to lookup alphabets> # corresponding to the index after shift> dict2>=> {>0> :>'Z'>,>1> :>'A'>,>2> :>'B'>,>3> :>'C'>,>4> :>'D'>,>5> :>'E'>,> >6> :>'F'>,>7> :>'G'>,>8> :>'H'>,>9> :>'I'>,>10> :>'J'>,> >11> :>'K'>,>12> :>'L'>,>13> :>'M'>,>14> :>'N'>,>15> :>'O'>,> >16> :>'P'>,>17> :>'Q'>,>18> :>'R'>,>19> :>'S'>,>20> :>'T'>,> >21> :>'U'>,>22> :>'V'>,>23> :>'W'>,>24> :>'X'>,>25> :>'Y'>}> # Function to encrypt the string> # according to the shift provided> def> encrypt(message, shift):> >cipher>=> ''> >for> letter>in> message:> ># checking for space> >if>(letter !>=> ' '>):> ># looks up the dictionary and> ># adds the shift to the index> >num>=> ( dict1[letter]>+> shift )>%> 26> ># looks up the second dictionary for> ># the shifted alphabets and adds them> >cipher>+>=> dict2[num]> >else>:> ># adds space> >cipher>+>=> ' '> >return> cipher> # Function to decrypt the string> # according to the shift provided> def> decrypt(message, shift):> >decipher>=> ''> >for> letter>in> message:> ># checks for space> >if>(letter !>=> ' '>):> ># looks up the dictionary and> ># subtracts the shift to the index> >num>=> ( dict1[letter]>-> shift>+> 26>)>%> 26> ># looks up the second dictionary for the> ># shifted alphabets and adds them> >decipher>+>=> dict2[num]> >else>:> ># adds space> >decipher>+>=> ' '> >return> decipher> # driver function to run the program> def> main():> ># use 'upper()' function to convert any lowercase characters to uppercase> >message>=> 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'> >shift>=> 13> >result>=> encrypt(message.upper(), shift)> >print> (result)> >message>=> 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'> >shift>=> 13> >result>=> decrypt(message.upper(), shift)> >print> (result)> # Executes the main function> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> >main()> |
>
>
C#
using> System;> using> System.Collections;> using> System.Collections.Generic;> using> System.Linq;> // C# program for the above approach> class> HelloWorld {> > >// Map to lookup the index of alphabets> >public> static> Dictionary<>char>,>int>>dict1 =>new> Dictionary<>char>,>int>>();> >// Map to lookup alphabets corresponding> >// to the index after shift> >public> static> Dictionary<>int>,>char>>dict2 =>new> Dictionary<>int>,>char>>();> >// Function to create map to lookup> >public> static> void> create_dict() {> >for>(>int> i = 1; i <27; i++)> >dict1.Add((>char>)(64 + i), i);> >dict2.Add(0,>'Z'>);> >for>(>int> i = 1; i <26; i++)> >dict2.Add(i, (>char>)(64 + i));> >}> >// Function to encrypt the string> >// according to the shift provided> >public> static> string> encrypt(>string> message,>int> shift) {> >string> cipher =>''>;> >for>(>int> i = 0; i // Checking for namespace if(message[i] != ' ') { // looks up the map and // adds the shift to the index int num = (dict1[message[i]] + shift) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them cipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space cipher += ' '; } } return cipher; } // Function to decrypt the string // according to the shift provided public static string decrypt(string message, int shift) { string decipher = ''; for(int i = 0; i // checks for space if(message[i] != ' ') { // looks up the map and // subtracts the shift to the index int num = (dict1[message[i]]- shift + 26) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them decipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space decipher += ' '; } } return decipher; } static void Main() { create_dict(); string message = 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'; int shift = 13; Console.WriteLine(encrypt(message, shift)); message = 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'; shift = 13; Console.WriteLine(decrypt(message, shift)); } } // The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.> |
>
>
Javascript
// Dictionary to lookup the index of alphabets> const dict1 = {>'A'>: 1,>'B'>: 2,>'C'>: 3,>'D'>: 4,>'E'>: 5,> >'F'>: 6,>'G'>: 7,>'H'>: 8,>'I'>: 9,>'J'>: 10,> >'K'>: 11,>'L'>: 12,>'M'>: 13,>'N'>: 14,>'O'>: 15,> >'P'>: 16,>'Q'>: 17,>'R'>: 18,>'S'>: 19,>'T'>: 20,> >'U'>: 21,>'V'>: 22,>'W'>: 23,>'X'>: 24,>'Y'>: 25,>'Z'>: 26};> // Dictionary to lookup alphabets> // corresponding to the index after shift> const dict2 = {0:>'Z'>, 1:>'A'>, 2:>'B'>, 3:>'C'>, 4:>'D'>, 5:>'E'>,> >6:>'F'>, 7:>'G'>, 8:>'H'>, 9:>'I'>, 10:>'J'>,> >11:>'K'>, 12:>'L'>, 13:>'M'>, 14:>'N'>, 15:>'O'>,> >16:>'P'>, 17:>'Q'>, 18:>'R'>, 19:>'S'>, 20:>'T'>,> >21:>'U'>, 22:>'V'>, 23:>'W'>, 24:>'X'>, 25:>'Y'>};> // Function to encrypt the string> // according to the shift provided> function> encrypt(message, shift) {> >let cipher =>''>;> >for> (let i = 0; i const letter = message[i]; // checking for space if (letter !== ' ') { // looks up the dictionary and // adds the shift to the index const num = (dict1[letter] + shift) % 26; // looks up the second dictionary for // the shifted alphabets and adds them cipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space cipher += ' '; } } return cipher; } // Function to decrypt the string // according to the shift provided function decrypt(message, shift) { let decipher = ''; for (let i = 0; i const letter = message[i]; // checks for space if (letter !== ' ') { // looks up the dictionary and // subtracts the shift to the index const num = (dict1[letter] - shift + 26) % 26; // looks up the second dictionary for the // shifted alphabets and adds them decipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space decipher += ' '; } } return decipher; } // driver function to run the program function main() { // use 'toUpperCase()' function to convert any lowercase characters to uppercase let message = 'GEEKS FOR GEEKS'; let shift = 13; let result = encrypt(message.toUpperCase(), shift); console.log(result); message = 'TRRXF SBE TRRXF'; shift = 13; result = decrypt(message.toUpperCase(), shift); console.log(result); } main(); // This code is contributed by adityashatmfh> |
>
>Uitvoer
TRRXF SBE TRRXF GEEKS FOR GEEKS>
Analyse: Het ROT13-cijfer is niet erg veilig, omdat het slechts een speciaal geval is van het Caesar-cijfer. Het Caesar-cijfer kan worden verbroken door frequentieanalyse of door gewoon alle 25 sleutels uit te proberen, terwijl het ROT13-cijfer kan worden verbroken door de letters slechts 13 plaatsen te verschuiven. Daarom heeft het geen praktisch nut.
dart lijst
Sollicitatie: ROT13 was begin jaren tachtig in gebruik in de nieuwsgroep net.jokes.
