In dit artikel bespreken we het Quicksort-algoritme. Ook de werkwijze van Quicksort is eenvoudig. Dit artikel zal zeer nuttig en interessant zijn voor studenten, aangezien zij tijdens hun examens met quicksort te maken kunnen krijgen. Het is dus belangrijk om het onderwerp te bespreken.
Sorteren is een manier om items op een systematische manier te ordenen. Quicksort is het veelgebruikte sorteeralgoritme dat zorgt voor n log n vergelijkingen in het gemiddelde geval voor het sorteren van een reeks van n elementen. Het is een sneller en zeer efficiënt sorteeralgoritme. Dit algoritme volgt de verdeel-en-heers-aanpak. Verdeel en heers is een techniek waarbij de algoritmen in deelproblemen worden opgedeeld, vervolgens de deelproblemen worden opgelost en de resultaten weer worden gecombineerd om het oorspronkelijke probleem op te lossen.
'kruskal's algoritme'
Verdeling: Kies in Divide eerst een draaielement. Verdeel of herschik daarna de array in twee subarrays, zodat elk element in de linker subarray kleiner is dan of gelijk is aan het draaielement en elk element in de rechter subarray groter is dan het draaielement.
Veroveren: Sorteer recursief twee subarrays met Quicksort.
Combineren: Combineer de reeds gesorteerde array.
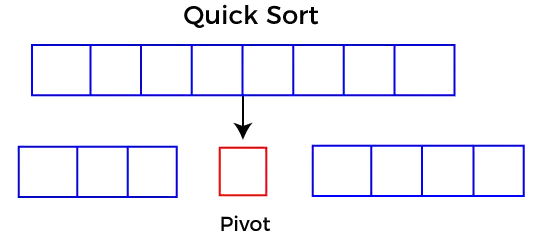
Quicksort kiest een element als draaipunt en verdeelt vervolgens de gegeven array rond het gekozen draaielement. Bij snel sorteren wordt een grote array verdeeld in twee arrays, waarbij de ene waarden bevat die kleiner zijn dan de opgegeven waarde (Pivot), en een andere array de waarden bevat die groter zijn dan de pivot.
Daarna worden de linker en rechter subarrays ook gepartitioneerd met behulp van dezelfde aanpak. Dit gaat door totdat het enkele element in de subarray blijft.
Het kiezen van de spil
Het kiezen van een goede pivot is noodzakelijk voor een snelle implementatie van quicksort. Het is echter typisch om een goed draaipunt te bepalen. Enkele manieren om een draaipunt te kiezen zijn als volgt:
- Draaipunt kan willekeurig zijn, d.w.z. selecteer het willekeurige draaipunt uit de gegeven array.
- Draaipunt kan het meest rechtse element van het meest linkse element van de gegeven array zijn.
- Selecteer mediaan als draaielement.
Algoritme
Algoritme:
QUICKSORT (array A, start, end) { 1 if (start <end) 2 3 4 5 6 { p="partition(A," start, end) quicksort (a, - 1) + 1, } < pre> <p> <strong>Partition Algorithm:</strong> </p> <p>The partition algorithm rearranges the sub-arrays in a place.</p> <pre> PARTITION (array A, start, end) { 1 pivot ? A[end] 2 i ? start-1 3 for j ? start to end -1 { 4 do if (A[j] <pivot) 1 5 6 7 8 9 { then i ? + swap a[i] with a[j] }} a[i+1] a[end] return i+1 } < pre> <h2>Working of Quick Sort Algorithm</h2> <p>Now, let's see the working of the Quicksort Algorithm.</p> <p>To understand the working of quick sort, let's take an unsorted array. It will make the concept more clear and understandable.</p> <p>Let the elements of array are -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-2.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>In the given array, we consider the leftmost element as pivot. So, in this case, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 27 and a[pivot] = 24.</p> <p>Since, pivot is at left, so algorithm starts from right and move towards left.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-3.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] <a[right], so algorithm moves forward one position towards left, i.e. -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-4.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 19, and a[pivot] = 24.</p> <p>Because, a[pivot] > a[right], so, algorithm will swap a[pivot] with a[right], and pivot moves to right, as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-5.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 19, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. Since, pivot is at right, so algorithm starts from left and moves to right.</p> <p>As a[pivot] > a[left], so algorithm moves one position to right as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-6.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 9, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] > a[left], so algorithm moves one position to right as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-7.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 29, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] <a[left], so, swap a[pivot] and a[left], now pivot is at left, i.e. -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-8.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Since, pivot is at left, so algorithm starts from right, and move to left. Now, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 29, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] <a[right], so algorithm moves one position to left, as -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-9.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 24, and a[right] = 14. As a[pivot] > a[right], so, swap a[pivot] and a[right], now pivot is at right, i.e. -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-10.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 14, and a[right] = 24. Pivot is at right, so the algorithm starts from left and move to right.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-11.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 24, and a[right] = 24. So, pivot, left and right are pointing the same element. It represents the termination of procedure.</p> <p>Element 24, which is the pivot element is placed at its exact position.</p> <p>Elements that are right side of element 24 are greater than it, and the elements that are left side of element 24 are smaller than it.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-12.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, in a similar manner, quick sort algorithm is separately applied to the left and right sub-arrays. After sorting gets done, the array will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-13.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <h2>Quicksort complexity</h2> <p>Now, let's see the time complexity of quicksort in best case, average case, and in worst case. We will also see the space complexity of quicksort.</p> <h3>1. Time Complexity</h3> <table class="table"> <tr> <th>Case</th> <th>Time Complexity</th> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Best Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Average Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Worst Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n<sup>2</sup>)</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <tr><td>Best Case Complexity -</td> In Quicksort, the best-case occurs when the pivot element is the middle element or near to the middle element. The best-case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n*logn)</strong> . </tr><tr><td>Average Case Complexity -</td> It occurs when the array elements are in jumbled order that is not properly ascending and not properly descending. The average case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n*logn)</strong> . </tr><tr><td>Worst Case Complexity -</td> In quick sort, worst case occurs when the pivot element is either greatest or smallest element. Suppose, if the pivot element is always the last element of the array, the worst case would occur when the given array is sorted already in ascending or descending order. The worst-case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n<sup>2</sup>)</strong> . </tr></ul> <p>Though the worst-case complexity of quicksort is more than other sorting algorithms such as <strong>Merge sort</strong> and <strong>Heap sort</strong> , still it is faster in practice. Worst case in quick sort rarely occurs because by changing the choice of pivot, it can be implemented in different ways. Worst case in quicksort can be avoided by choosing the right pivot element.</p> <h3>2. Space Complexity</h3> <table class="table"> <tr> <td> <strong>Space Complexity</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Stable</strong> </td> <td>NO</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <li>The space complexity of quicksort is O(n*logn).</li> </ul> <h2>Implementation of quicksort</h2> <p>Now, let's see the programs of quicksort in different programming languages.</p> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in C language.</p> <pre> #include /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 27 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) printf('%d ', a[i]); main() 24, 9, 29, 14, 19, }; n="sizeof(a)" sizeof(a[0]); printf('before sorting elements are
'); printarr(a, n); 0, printf('
after 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-14.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quick sort in C++ language.</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 26 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) cout< <a[i]<< ' '; main() 23, 8, 28, 13, 18, }; n="sizeof(a)" sizeof(a[0]); cout<<'before sorting elements are
'; printarr(a, n); 0, cout<<'
after 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-15.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in python.</p> <pre> #function that consider last element as pivot, #place the pivot at its exact position, and place #smaller elements to left of pivot and greater #elements to right of pivot. def partition (a, start, end): i = (start - 1) pivot = a[end] # pivot element for j in range(start, end): # If current element is smaller than or equal to the pivot if (a[j] <= 1 pivot): i="i" + a[i], a[j]="a[j]," a[i] a[i+1], a[end]="a[end]," a[i+1] return (i 1) # function to implement quick sort def quick(a, start, end): a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, end="Ending" index if (start < p="partition(a," end) is partitioning - 1, printarr(a): print the array for in range(len(a)): (a[i], ) a="[68," 13, 49, 58] print('before sorting elements are ') printarr(a) 0, len(a)-1) print('
after pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-16.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in Java.</p> <pre> public class Quick { /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 25 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) system.out.print(a[i] ' '); public static main(string[] args) 13, 18, 27, 2, 19, }; n="a.length;" system.out.println('
before sorting elements are q1="new" quick(); q1.printarr(a, n); q1.quick(a, 0, system.out.println('
after system.out.println(); pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <p>After the execution of above code, the output will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-17.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quick sort in php.</p> <pre> <?php /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ function partition (&$a, $start, $end) { $pivot = $a[$end]; // pivot element $i = ($start - 1); for ($j = $start; $j <= $end - 1; $j++) { // If current element is smaller than the pivot if ($a[$j] < $pivot) { $i++; // increment index of smaller element $t = $a[$i]; $a[$i] = $a[$j]; $a[$j] = $t; } } $t = $a[$i+1]; $a[$i+1] = $a[$end]; $a[$end] = $t; return ($i + 1); } /* function to implement quick sort */ function quick(&$a, $start, $end) /* a[] = array to be sorted, start = Starting index, end = Ending index */ { if ($start < $end) { $p = partition($a, $start, $end); //p is partitioning index quick($a, $start, $p - 1); quick($a, $p + 1, $end); } } function printArray($a, $n) { for($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) { print_r($a[$i]); echo ' '; } } $a = array( 89, 47, 2, 17, 8, 19 ); $n = count($a); echo 'Before sorting array elements are - <br>'; printArray($a, $n); quick($a, 0, $n - 1); echo ' <br> After sorting array elements are - <br>'; printArray($a, $n); ?> </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <p>After the execution of above code, the output will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-18.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>So, that's all about the article. Hope the article will be helpful and informative to you.</p> <p>This article was not only limited to the algorithm. Along with the algorithm, we have also discussed the quick sort complexity, working, and implementation in different programming languages.</p> <hr></=></pre></=></pre></=></pre></=></pre></a[right],></p></a[left],></p></a[right],></p></pivot)></pre></end)> Uitvoer
Na de uitvoering van bovenstaande code zal de uitvoer zijn:

Dus dat is alles over het artikel. Ik hoop dat het artikel nuttig en informatief voor u zal zijn.
converteer tekenreeks naar jsonobject Java
Dit artikel beperkte zich niet alleen tot het algoritme. Naast het algoritme hebben we ook de complexiteit, werking en implementatie van snel sorteren in verschillende programmeertalen besproken.
