 #practiceLinkDiv {weergave: geen! belangrijk; }
#practiceLinkDiv {weergave: geen! belangrijk; }Gegeven een reeks punten as en een lijn als ax+by+c = 0. We moeten een punt op een gegeven lijn vinden waarvoor de som van de afstanden tot een gegeven reeks punten minimaal is.
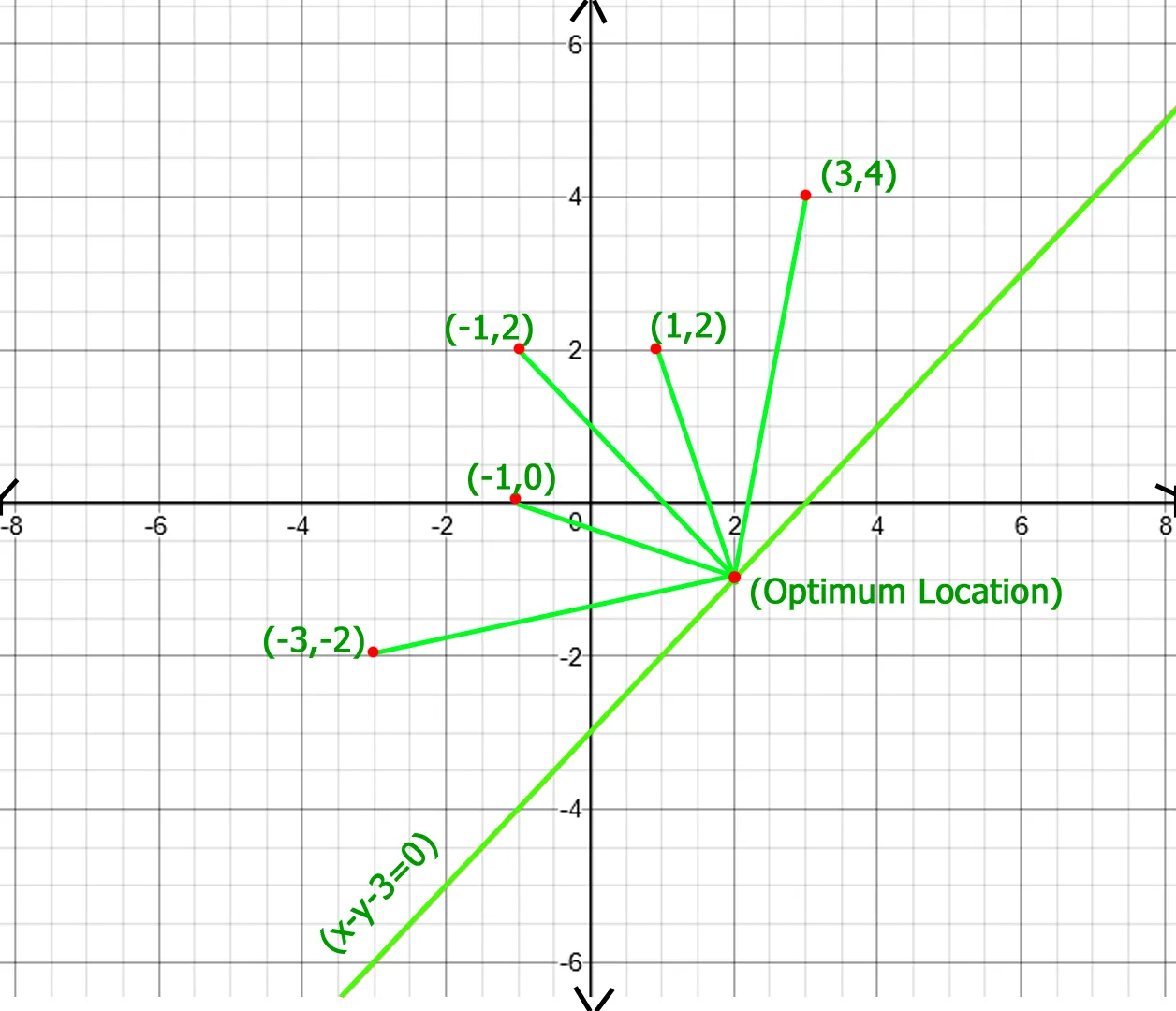
Voorbeeld:
Linux run-opdracht
In above figure optimum location of point of x - y - 3 = 0 line is (2 -1) whose total distance with other points is 20.77 which is minimum obtainable total distance.Recommended Practice Optimale locatie van het punt om de totale afstand te minimaliseren Probeer het!
Als we één punt op een gegeven lijn op oneindige afstand nemen, zullen de totale afstandskosten oneindig zijn. Als we dit punt op de lijn naar bepaalde punten verplaatsen, beginnen de totale afstandskosten te dalen en na enige tijd begint het weer te stijgen, wat reikt tot oneindig aan het andere oneindige uiteinde van de lijn, dus de afstandskostencurve ziet eruit als een U-curve en we moeten de onderste waarde van deze U-curve vinden.
Omdat de U-curve niet monotoon stijgt of daalt, kunnen we geen binair zoeken gebruiken om het onderste punt te vinden. Hier gebruiken we ternair zoeken om het onderste punt te vinden. ternair zoeken slaat een derde van de zoekruimte over bij elke iteratie. U kunt meer lezen over ternair zoeken hier .
De oplossing verloopt dus als volgt: we beginnen met laag en hoog, respectievelijk geïnitialiseerd als enkele kleinste en grootste waarden. Vervolgens beginnen we met iteratie. In elke iteratie berekenen we twee middentonen midden1 en midden2 die de 1/3e en 2/3e positie in de zoekruimte vertegenwoordigen. We berekenen de totale afstand van alle punten met midden1 en midden2 en werken laag of hoog bij door deze afstandskosten te vergelijken. Deze iteratie gaat door totdat laag en hoog ongeveer gelijk worden.
analoge communicatieC++
// C/C++ program to find optimum location and total cost #include
// A Java program to find optimum location // and total cost class GFG { static double sq(double x) { return ((x) * (x)); } static int EPS = (int)(1e-6) + 1; static int N = 5; // structure defining a point static class point { int x y; point() {} public point(int x int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } }; // structure defining a line of ax + by + c = 0 form static class line { int a b c; public line(int a int b int c) { this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; } }; // method to get distance of point (x y) from point p static double dist(double x double y point p) { return Math.sqrt(sq(x - p.x) + sq(y - p.y)); } /* Utility method to compute total distance all points when choose point on given line has x-coordinate value as X */ static double compute(point p[] int n line l double X) { double res = 0; // calculating Y of chosen point by line equation double Y = -1 * (l.c + l.a * X) / l.b; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) res += dist(X Y p[i]); return res; } // Utility method to find minimum total distance static double findOptimumCostUtil(point p[] int n line l) { double low = -1e6; double high = 1e6; // loop until difference between low and high // become less than EPS while ((high - low) > EPS) { // mid1 and mid2 are representative x // co-ordiantes of search space double mid1 = low + (high - low) / 3; double mid2 = high - (high - low) / 3; double dist1 = compute(p n l mid1); double dist2 = compute(p n l mid2); // if mid2 point gives more total distance // skip third part if (dist1 < dist2) high = mid2; // if mid1 point gives more total distance // skip first part else low = mid1; } // compute optimum distance cost by sending average // of low and high as X return compute(p n l (low + high) / 2); } // method to find optimum cost static double findOptimumCost(int points[][] line l) { point[] p = new point[N]; // converting 2D array input to point array for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) p[i] = new point(points[i][0] points[i][1]); return findOptimumCostUtil(p N l); } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { line l = new line(1 -1 -3); int points[][] = { { -3 -2 } { -1 0 } { -1 2 } { 1 2 } { 3 4 } }; System.out.println(findOptimumCost(points l)); } } // This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
# A Python3 program to find optimum location # and total cost import math class Optimum_distance: # Class defining a point class Point: def __init__(self x y): self.x = x self.y = y # Class defining a line of ax + by + c = 0 form class Line: def __init__(self a b c): self.a = a self.b = b self.c = c # Method to get distance of point # (x y) from point p def dist(self x y p): return math.sqrt((x - p.x) ** 2 + (y - p.y) ** 2) # Utility method to compute total distance # all points when choose point on given # line has x-coordinate value as X def compute(self p n l x): res = 0 y = -1 * (l.a*x + l.c) / l.b # Calculating Y of chosen point # by line equation for i in range(n): res += self.dist(x y p[i]) return res # Utility method to find minimum total distance def find_Optimum_cost_untill(self p n l): low = -1e6 high = 1e6 eps = 1e-6 + 1 # Loop until difference between low # and high become less than EPS while((high - low) > eps): # mid1 and mid2 are representative x # co-ordiantes of search space mid1 = low + (high - low) / 3 mid2 = high - (high - low) / 3 dist1 = self.compute(p n l mid1) dist2 = self.compute(p n l mid2) # If mid2 point gives more total # distance skip third part if (dist1 < dist2): high = mid2 # If mid1 point gives more total # distance skip first part else: low = mid1 # Compute optimum distance cost by # sending average of low and high as X return self.compute(p n l (low + high) / 2) # Method to find optimum cost def find_Optimum_cost(self p l): n = len(p) p_arr = [None] * n # Converting 2D array input to point array for i in range(n): p_obj = self.Point(p[i][0] p[i][1]) p_arr[i] = p_obj return self.find_Optimum_cost_untill(p_arr n l) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': obj = Optimum_distance() l = obj.Line(1 -1 -3) p = [ [ -3 -2 ] [ -1 0 ] [ -1 2 ] [ 1 2 ] [ 3 4 ] ] print(obj.find_Optimum_cost(p l)) # This code is contributed by Sulu_mufi
// C# program to find optimum location // and total cost using System; class GFG { static double sq(double x) { return ((x) * (x)); } static int EPS = (int)(1e-6) + 1; static int N = 5; // structure defining a point public class point { public int x y; public point() {} public point(int x int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } }; // structure defining a line // of ax + by + c = 0 form public class line { public int a b c; public line(int a int b int c) { this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; } }; // method to get distance of // point (x y) from point p static double dist(double x double y point p) { return Math.Sqrt(sq(x - p.x) + sq(y - p.y)); } /* Utility method to compute total distance of all points when choose point on given line has x-coordinate value as X */ static double compute(point[] p int n line l double X) { double res = 0; // calculating Y of chosen point // by line equation double Y = -1 * (l.c + l.a * X) / l.b; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) res += dist(X Y p[i]); return res; } // Utility method to find minimum total distance static double findOptimumCostUtil(point[] p int n line l) { double low = -1e6; double high = 1e6; // loop until difference between // low and high become less than EPS while ((high - low) > EPS) { // mid1 and mid2 are representative // x co-ordiantes of search space double mid1 = low + (high - low) / 3; double mid2 = high - (high - low) / 3; double dist1 = compute(p n l mid1); double dist2 = compute(p n l mid2); // if mid2 point gives more total distance // skip third part if (dist1 < dist2) high = mid2; // if mid1 point gives more total distance // skip first part else low = mid1; } // compute optimum distance cost by // sending average of low and high as X return compute(p n l (low + high) / 2); } // method to find optimum cost static double findOptimumCost(int[ ] points line l) { point[] p = new point[N]; // converting 2D array input to point array for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) p[i] = new point(points[i 0] points[i 1]); return findOptimumCostUtil(p N l); } // Driver Code public static void Main(String[] args) { line l = new line(1 -1 -3); int[ ] points = { { -3 -2 } { -1 0 } { -1 2 } { 1 2 } { 3 4 } }; Console.WriteLine(findOptimumCost(points l)); } } // This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
<script> // A JavaScript program to find optimum location // and total cost function sq(x) { return x*x; } let EPS = (1e-6) + 1; let N = 5; // structure defining a point class point { constructor(xy) { this.x=x; this.y=y; } } // structure defining a line of ax + by + c = 0 form class line { constructor(abc) { this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; } } // method to get distance of point (x y) from point p function dist(xyp) { return Math.sqrt(sq(x - p.x) + sq(y - p.y)); } /* Utility method to compute total distance all points when choose point on given line has x-coordinate value as X */ function compute(pnlX) { let res = 0; // calculating Y of chosen point by line equation let Y = -1 * (l.c + l.a * X) / l.b; for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) res += dist(X Y p[i]); return res; } // Utility method to find minimum total distance function findOptimumCostUtil(pnl) { let low = -1e6; let high = 1e6; // loop until difference between low and high // become less than EPS while ((high - low) > EPS) { // mid1 and mid2 are representative x // co-ordiantes of search space let mid1 = low + (high - low) / 3; let mid2 = high - (high - low) / 3; let dist1 = compute(p n l mid1); let dist2 = compute(p n l mid2); // if mid2 point gives more total distance // skip third part if (dist1 < dist2) high = mid2; // if mid1 point gives more total distance // skip first part else low = mid1; } // compute optimum distance cost by sending average // of low and high as X return compute(p n l (low + high) / 2); } // method to find optimum cost function findOptimumCost(pointsl) { let p = new Array(N); // converting 2D array input to point array for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) p[i] = new point(points[i][0] points[i][1]); return findOptimumCostUtil(p N l); } // Driver Code let l = new line(1 -1 -3); let points= [[ -3 -2 ] [ -1 0 ] [ -1 2 ] [ 1 2 ] [ 3 4 ]]; document.write(findOptimumCost(points l)); // This code is contributed by rag2127 </script>
Uitvoer
20.7652
Tijdcomplexiteit: Op2)
Hulpruimte: Op)
