Gegeven een binaire boom de taak is om omdraaien de binaire boom richting de goede richting ndat is rechtsom.
Java-logo
Invoer:
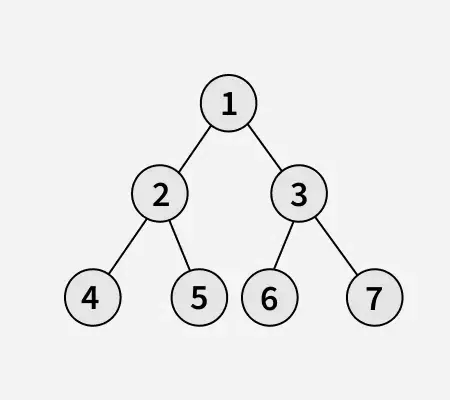
Uitgang:
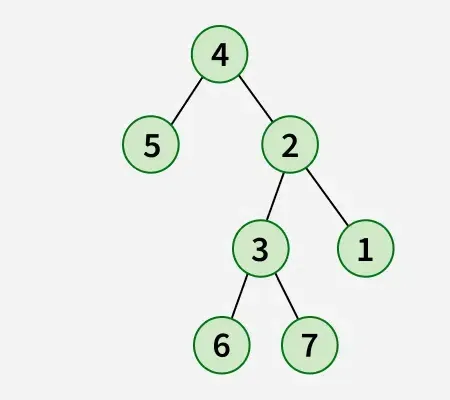
Java voegt tekenreeksen samenUitleg: Bij de omdraaioperatie wordt het meest linkse knooppunt de wortel van de omgedraaide boom en wordt de ouder het rechterkind en het rechterzusje wordt het linkerkind. Hetzelfde moet recursief voor alle meest linkse knooppunten worden gedaan.
Inhoudsopgave
- [Verwachte aanpak - 1] Recursie gebruiken - O(n) tijd en O(n) ruimte
- [Verwachte aanpak - 2] Iteratieve aanpak - O(n) Tijd en O(1) Ruimte
[Verwachte aanpak - 1] Recursie gebruiken - O(n) tijd en O(n) ruimte
Het idee is om recursief draai de binaire boom om door de links En rechts subbomen van elk knooppunt. Na het omdraaien wordt de structuur van de boom omgekeerd en wordt de nieuwe wortel van de omgevallen boom zal het oorspronkelijke meest linkse bladknooppunt zijn.
Hieronder vindt u de belangrijkste rotatiecode van een subboom:
- wortel->links->links = wortel->rechts
- wortel->links->rechts = wortel
- root->links = NULL
- root->rechts = NULL
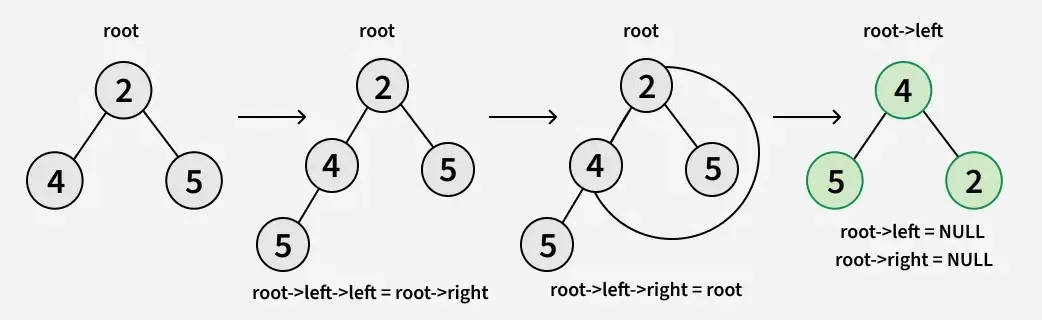
Hieronder vindt u de implementatie van de bovenstaande aanpak:
'bankiersalgoritme'C++
// C++ program to flip a binary tree // using recursion #include
// Java program to flip a binary tree // using recursion class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root) { // Base cases if (root == null) return root; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root; // Recursively call the same method Node flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root.left.left = root.right; root.left.right = root; root.left = root.right = null; return flippedRoot; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void printLevelOrder(Node root) { // Base Case if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal java.util.Queue<Node> q = new java.util.LinkedList<>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.add(root); while (!q.isEmpty()) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.size(); // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.poll(); System.out.print(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.add(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.add(node.right); nodeCount--; } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(root); } }
# Python program to flip a binary # tree using recursion class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None def flipBinaryTree(root): # Base cases if root is None: return root if root.left is None and root.right is None: return root # Recursively call the same method flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left) # Rearranging main root Node after returning # from recursive call root.left.left = root.right root.left.right = root root.left = root.right = None return flippedRoot # Iterative method to do level order # traversal line by line def printLevelOrder(root): # Base Case if root is None: return # Create an empty queue for # level order traversal queue = [] queue.append(root) while queue: nodeCount = len(queue) while nodeCount > 0: node = queue.pop(0) print(node.data end=' ') if node.left is not None: queue.append(node.left) if node.right is not None: queue.append(node.right) nodeCount -= 1 print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Make a binary tree # # 1 # / # 2 3 # / # 4 5 root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.right.left = Node(4) root.right.right = Node(5) root = flipBinaryTree(root) printLevelOrder(root)
// C# program to flip a binary tree // using recursion using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node FlipBinaryTree(Node root) { if (root == null) return root; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root; // Recursively call the same method Node flippedRoot = FlipBinaryTree(root.left); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root.left.left = root.right; root.left.right = root; root.left = root.right = null; return flippedRoot; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void PrintLevelOrder(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.Enqueue(root); while (q.Count > 0) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.Count; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.Dequeue(); Console.Write(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.Enqueue(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.Enqueue(node.right); nodeCount--; } Console.WriteLine(); } } static void Main(string[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = FlipBinaryTree(root); PrintLevelOrder(root); } }
// JavaScript program to flip a binary // tree using recursion class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Method to flip the binary tree function flipBinaryTree(root) { if (root === null) return root; if (root.left === null && root.right === null) return root; // Recursively call the same method const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root.left.left = root.right; root.left.right = root; root.left = root.right = null; return flippedRoot; } // Iterative method to do level order traversal // line by line function printLevelOrder(root) { if (root === null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal const queue = [root]; while (queue.length > 0) { let nodeCount = queue.length; while (nodeCount > 0) { const node = queue.shift(); console.log(node.data + ' '); if (node.left !== null) queue.push(node.left); if (node.right !== null) queue.push(node.right); nodeCount--; } console.log(); } } // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(flippedRoot);
Uitvoer
2 3 1 4 5
[Verwachte aanpak - 2] Iteratieve aanpak - O(n) Tijd en O(n) Ruimte
De iteratieve oplossing volgt dezelfde aanpak als de recursief Het enige waar we op moeten letten is besparing de knooppuntinformatie die zal zijn overwritten .
Hieronder vindt u de implementatie van de bovenstaande aanpak:
C++// C++ program to flip a binary tree using // iterative approach #include
// Java program to flip a binary tree // using iterative approach class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root) { // Initializing the pointers to do the // swapping and storing states Node curr = root; Node next = null; Node prev = null; Node ptr = null; while (curr != null) { // Pointing the next pointer to // the current next of left next = curr.left; // Making the right child of // prev as curr left child curr.left = ptr; // Storing the right child // of curr in ptr ptr = curr.right; curr.right = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void printLevelOrder(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal java.util.Queue<Node> q = new java.util.LinkedList<>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize // height q.add(root); while (!q.isEmpty()) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.size(); // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.poll(); System.out.print(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.add(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.add(node.right); nodeCount--; } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(root); } }
# Python program to flip a binary tree # using iterative approach class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None # Method to flip the binary tree # iteratively def flip_binary_tree(root): # Initializing the pointers to do # the swapping and storing states curr = root next = None prev = None ptr = None while curr is not None: # Pointing the next pointer to the # current next of left next = curr.left # Making the right child of prev # as curr left child curr.left = ptr # Storing the right child of # curr in ptr ptr = curr.right curr.right = prev prev = curr curr = next return prev # Iterative method to do level order # traversal line by line def printLevelOrder(root): if root is None: return # Create an empty queue for # level order traversal queue = [] queue.append(root) while queue: nodeCount = len(queue) while nodeCount > 0: node = queue.pop(0) print(node.data end=' ') if node.left is not None: queue.append(node.left) if node.right is not None: queue.append(node.right) nodeCount -= 1 print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Make a binary tree # # 1 # / # 2 3 # / # 4 5 root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.right.left = Node(4) root.right.right = Node(5) root = flip_binary_tree(root) printLevelOrder(root)
// C# program to flip a binary tree // using iterative approach using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node FlipBinaryTree(Node root) { // Initializing the pointers to // do the swapping and storing states Node curr = root; Node next = null; Node prev = null; Node ptr = null; while (curr != null) { // Pointing the next pointer to // the current next of left next = curr.left; // Making the right child of prev // as curr left child curr.left = ptr; // Storing the right child // of curr in ptr ptr = curr.right; curr.right = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void PrintLevelOrder(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for // level order traversal Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.Enqueue(root); while (q.Count > 0) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.Count; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.Dequeue(); Console.Write(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.Enqueue(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.Enqueue(node.right); nodeCount--; } Console.WriteLine(); } } static void Main(string[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = FlipBinaryTree(root); PrintLevelOrder(root); } }
// JavaScript program to flip a binary // tree using iterative approach class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } function flipBinaryTree(root) { // Initializing the pointers to do the // swapping and storing states let curr = root; let next = null; let prev = null; let ptr = null; while (curr !== null) { // Pointing the next pointer to the // current next of left next = curr.left; // Making the right child of prev // as curr left child curr.left = ptr; // Storing the right child of // curr in ptr ptr = curr.right; curr.right = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line function printLevelOrder(root) { if (root === null) return; // Create an empty queue for // level order traversal const queue = [root]; while (queue.length > 0) { let nodeCount = queue.length; while (nodeCount > 0) { const node = queue.shift(); console.log(node.data + ' '); if (node.left !== null) queue.push(node.left); if (node.right !== null) queue.push(node.right); nodeCount--; } console.log(); } } // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(flippedRoot);
Uitvoer
2 3 1 4 5



